Histo-Genomic Knowledge Distillation For Cancer Prognosis From Histopathology Whole Slide Images
Paper and Code
Mar 18, 2024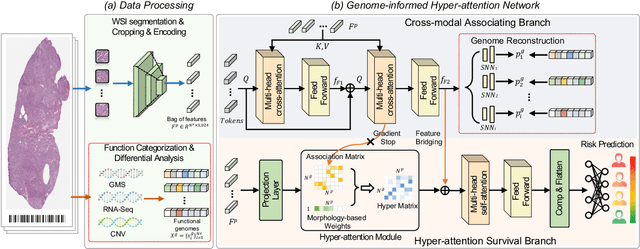
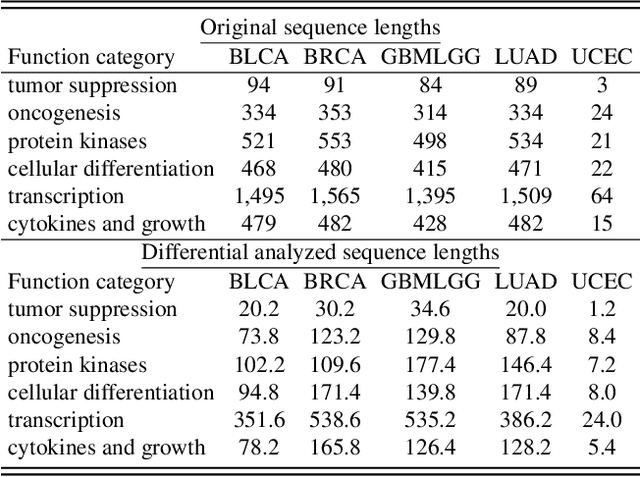
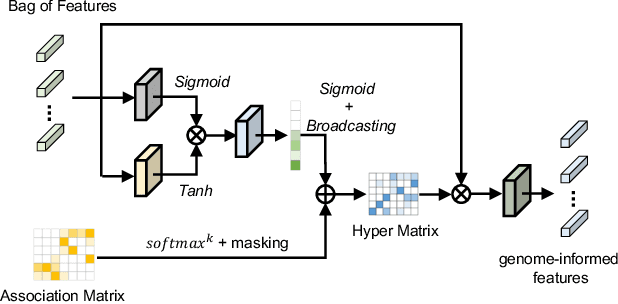
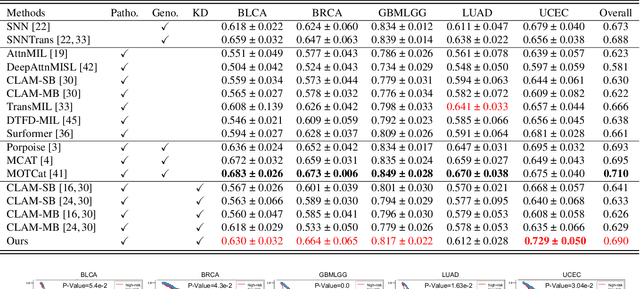
Histo-genomic multi-modal methods have recently emerged as a powerful paradigm, demonstrating significant potential for improving cancer prognosis. However, genome sequencing, unlike histopathology imaging, is still not widely accessible in underdeveloped regions, limiting the application of these multi-modal approaches in clinical settings. To address this, we propose a novel Genome-informed Hyper-Attention Network, termed G-HANet, which is capable of effectively distilling the histo-genomic knowledge during training to elevate uni-modal whole slide image (WSI)-based inference for the first time. Compared with traditional knowledge distillation methods (i.e., teacher-student architecture) in other tasks, our end-to-end model is superior in terms of training efficiency and learning cross-modal interactions. Specifically, the network comprises the cross-modal associating branch (CAB) and hyper-attention survival branch (HSB). Through the genomic data reconstruction from WSIs, CAB effectively distills the associations between functional genotypes and morphological phenotypes and offers insights into the gene expression profiles in the feature space. Subsequently, HSB leverages the distilled histo-genomic associations as well as the generated morphology-based weights to achieve the hyper-attention modeling of the patients from both histopathology and genomic perspectives to improve cancer prognosis. Extensive experiments are conducted on five TCGA benchmarking datasets and the results demonstrate that G-HANet significantly outperforms the state-of-the-art WSI-based methods and achieves competitive performance with genome-based and multi-modal methods. G-HANet is expected to be explored as a useful tool by the research community to address the current bottleneck of insufficient histo-genomic data pairing in the context of cancer prognosis and precision oncology.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge