Ground Truth Bias in External Cluster Validity Indices
Paper and Code
Jun 17, 2016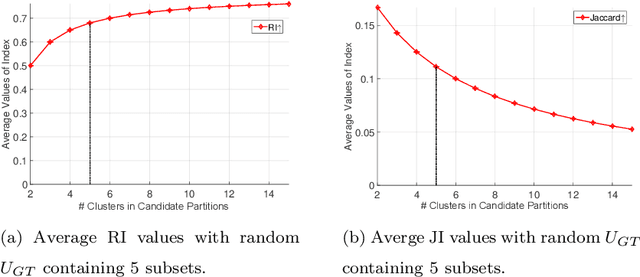
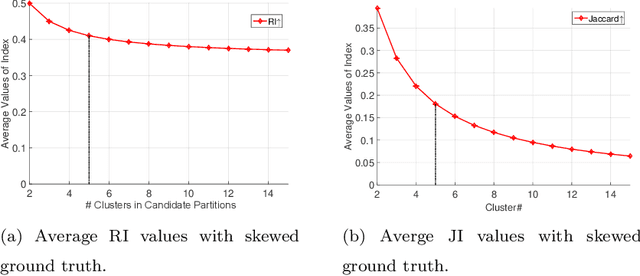

It has been noticed that some external CVIs exhibit a preferential bias towards a larger or smaller number of clusters which is monotonic (directly or inversely) in the number of clusters in candidate partitions. This type of bias is caused by the functional form of the CVI model. For example, the popular Rand index (RI) exhibits a monotone increasing (NCinc) bias, while the Jaccard Index (JI) index suffers from a monotone decreasing (NCdec) bias. This type of bias has been previously recognized in the literature. In this work, we identify a new type of bias arising from the distribution of the ground truth (reference) partition against which candidate partitions are compared. We call this new type of bias ground truth (GT) bias. This type of bias occurs if a change in the reference partition causes a change in the bias status (e.g., NCinc, NCdec) of a CVI. For example, NCinc bias in the RI can be changed to NCdec bias by skewing the distribution of clusters in the ground truth partition. It is important for users to be aware of this new type of biased behaviour, since it may affect the interpretations of CVI results. The objective of this article is to study the empirical and theoretical implications of GT bias. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first extensive study of such a property for external cluster validity indices.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge