GPT Paternity Test: GPT Generated Text Detection with GPT Genetic Inheritance
Paper and Code
May 21, 2023
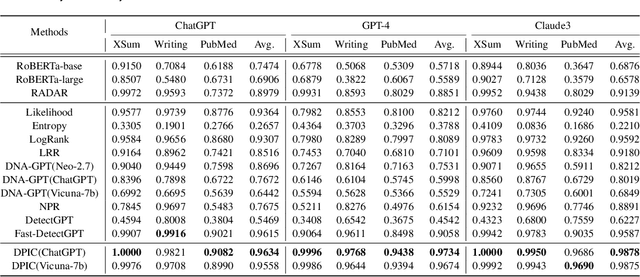
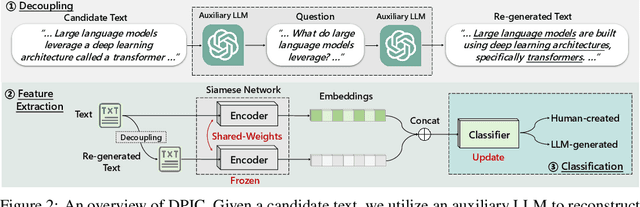
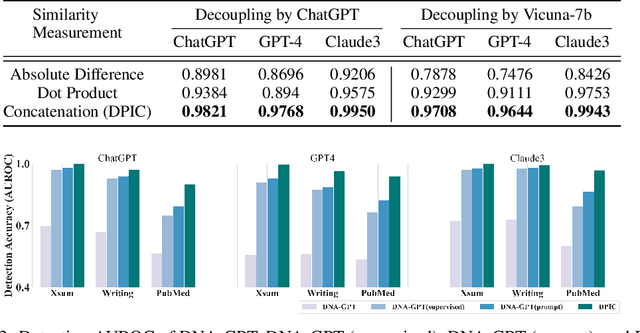
Large Language Models (LLMs) can generate texts that carry the risk of various misuses, including plagiarism, planting fake reviews on e-commerce platforms, or creating fake social media postings that can sway election results. Detecting whether a text is machine-generated has thus become increasingly important. While machine-learning-based detection strategies exhibit superior performance, they often lack generalizability, limiting their practicality. In this work, we introduce GPT Paternity Test (GPT-Pat), which reliably detects machine-generated text across varied datasets. Given a text under scrutiny, we leverage ChatGPT to generate a corresponding question and provide a re-answer to the question. By comparing the similarity between the original text and the generated re-answered text, it can be determined whether the text is machine-generated. GPT-Pat consists of a Siamese network to compute the similarity between the original text and the generated re-answered text and a binary classifier. Our method achieved an average accuracy of 94.57% on four generalization test sets, surpassing the state-of-the-art RoBERTa-based method by 12.34%. The accuracy drop of our method is only about half of that of the RoBERTa-based method when it is attacked by re-translation and polishing.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge