From Local SGD to Local Fixed Point Methods for Federated Learning
Paper and Code
Apr 03, 2020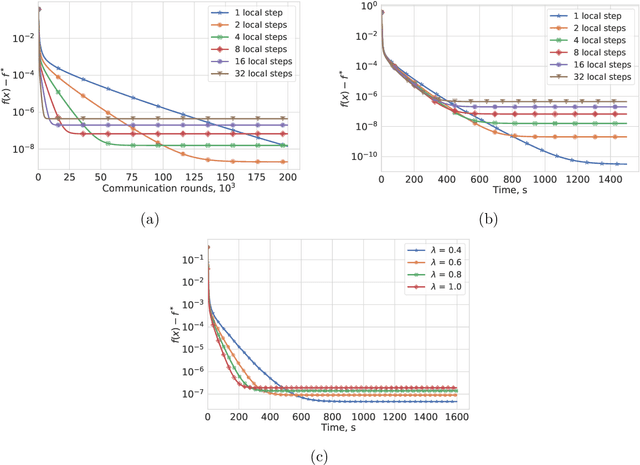
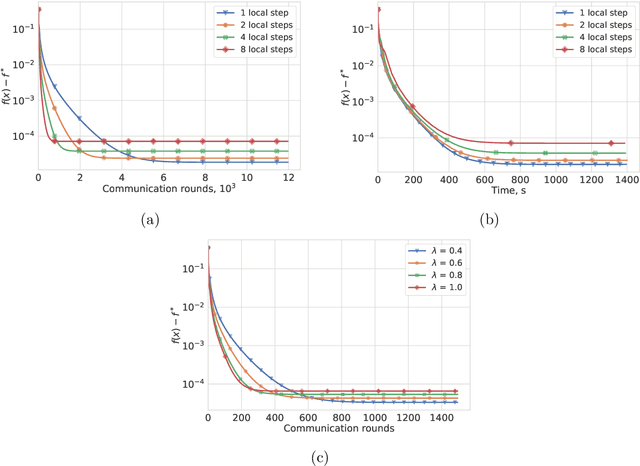
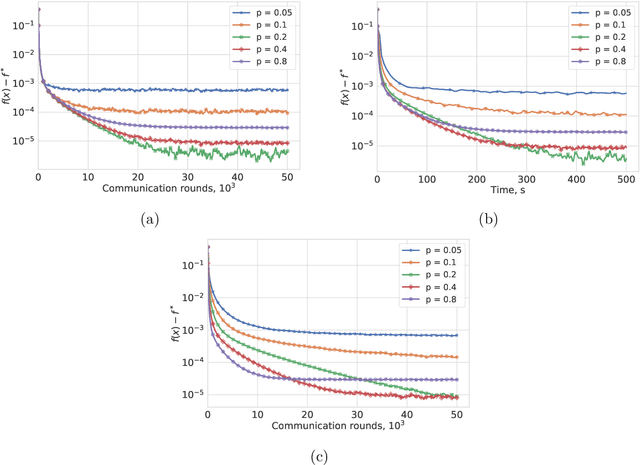
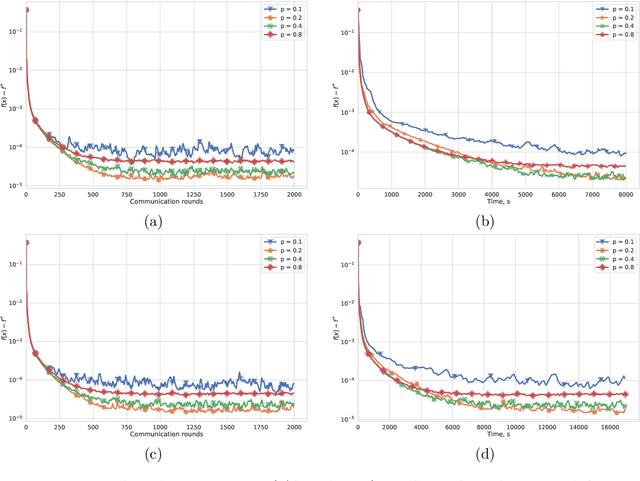
Most algorithms for solving optimization problems or finding saddle points of convex-concave functions are fixed point algorithms. In this work we consider the generic problem of finding a fixed point of an average of operators, or an approximation thereof, in a distributed setting. Our work is motivated by the needs of federated learning. In this context, each local operator models the computations done locally on a mobile device. We investigate two strategies to achieve such a consensus: one based on a fixed number of local steps, and the other based on randomized computations. In both cases, the goal is to limit communication of the locally-computed variables, which is often the bottleneck in distributed frameworks. We perform convergence analysis of both methods and conduct a number of experiments highlighting the benefits of our approach.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge