FLEXTAF: Enhancing Table Reasoning with Flexible Tabular Formats
Paper and Code
Aug 16, 2024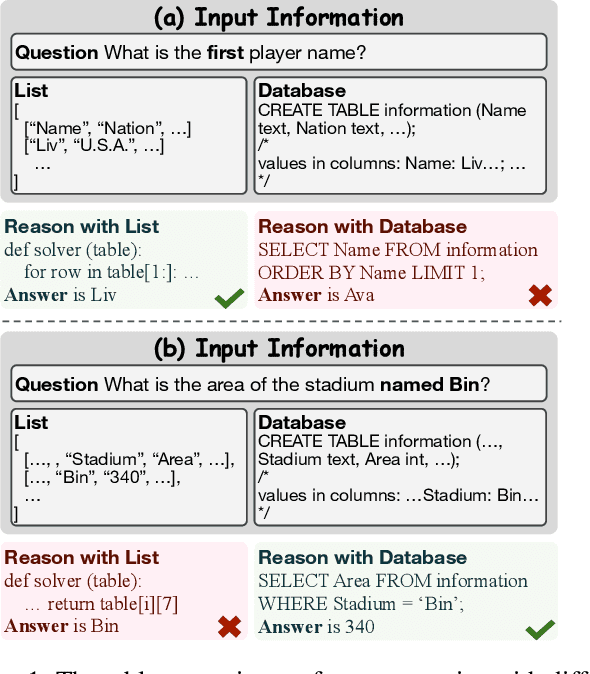
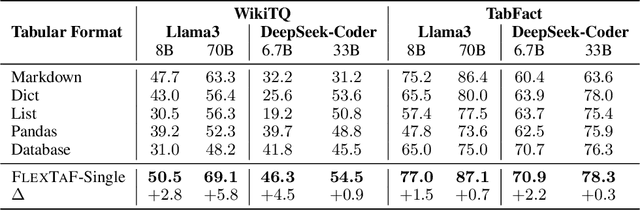
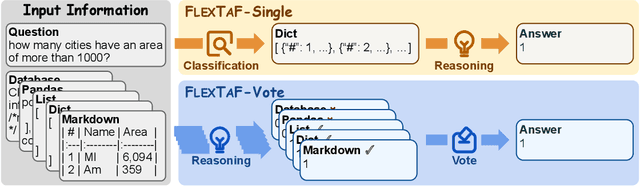
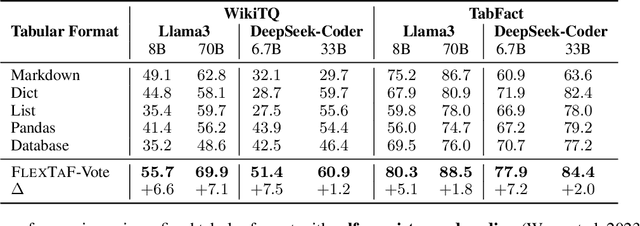
The table reasoning task aims to answer the question according to the given table. Currently, using Large Language Models (LLMs) is the predominant method for table reasoning. Most existing methods employ a fixed tabular format to represent the table, which could limit the performance. Given that each instance requires different capabilities and models possess varying abilities, we assert that different instances and models suit different tabular formats. We prove the aforementioned claim through quantitative analysis of experimental results, where different instances and models achieve different performances using various tabular formats. Building on this discussion, we propose FLEXTAF-Single and FLEXTAF-Vote to enhance table reasoning performance by employing flexible tabular formats. Specifically, (i) FLEXTAF-Single trains a classifier to predict the most suitable tabular format based on the instance and the LLM. (ii) FLEXTAF-Vote integrates the results across different formats. Our experiments on WikiTableQuestions and TabFact reveal significant improvements, with average gains of 2.3% and 4.8% compared to the best performance achieved using a fixed tabular format with greedy decoding and self-consistency decoding, thereby validating the effectiveness of our methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge