Federated Multi-Mini-Batch: An Efficient Training Approach to Federated Learning in Non-IID Environments
Paper and Code
Nov 13, 2020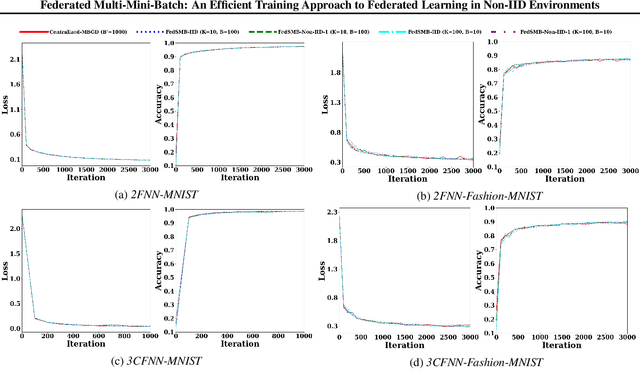
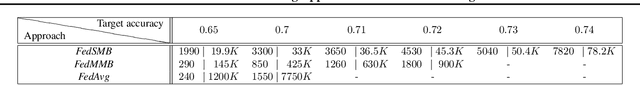
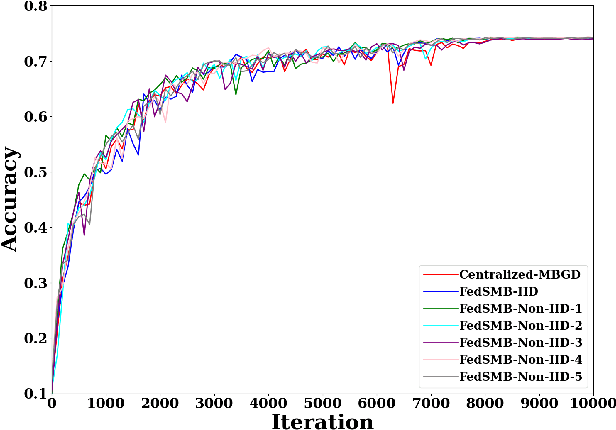
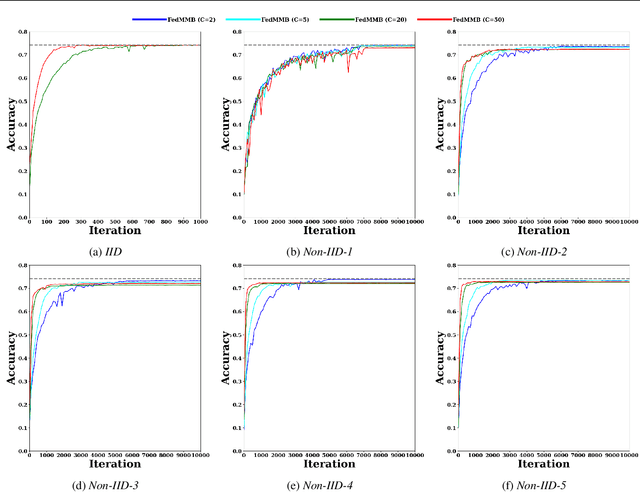
Federated learning is a well-established approach to privacy-preserving training of a joint model on heavily distributed data. Federated averaging (FedAvg) is a well-known communication-efficient algorithm for federated learning, which performs well if the data distribution across the clients is independently and identically distributed (IID). However, FedAvg provides a lower accuracy and still requires a large number of communication rounds to achieve a target accuracy when it comes to Non-IID environments. To address the former limitation, we present federated single mini-batch (FedSMB), where the clients train the model on a single mini-batch from their dataset in each iteration. We show that FedSMB achieves the accuracy of the centralized training in Non-IID configurations, but in a considerable number of iterations. To address the latter limitation, we introduce federated multi-mini-batch (FedMMB) as a generalization of FedSMB, where the clients train the model on multiple mini-batches (specified by the batch count) in each communication round. FedMMB decouples the batch size from the batch count and provides a trade-off between the accuracy and communication efficiency in Non-IID settings. This is not possible with FedAvg, in which a single parameter determines both the batch size and batch count. The simulation results illustrate that FedMMB outperforms FedAvg in terms of the accuracy, communication efficiency, as well as computational efficiency and is an efficient training approach to federated learning in Non-IID environments.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge