FactGraph: Evaluating Factuality in Summarization with Semantic Graph Representations
Paper and Code
Apr 13, 2022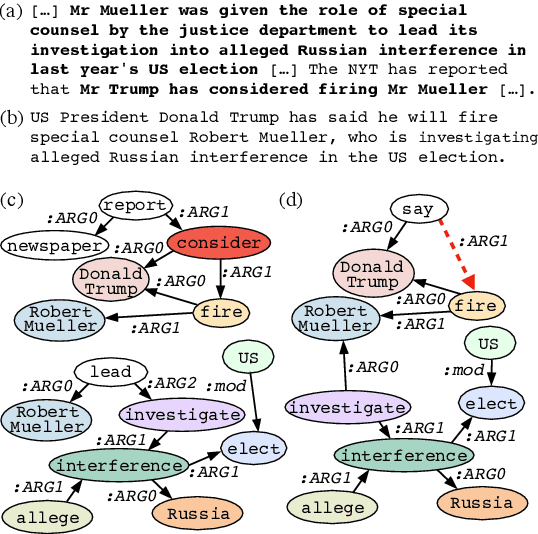
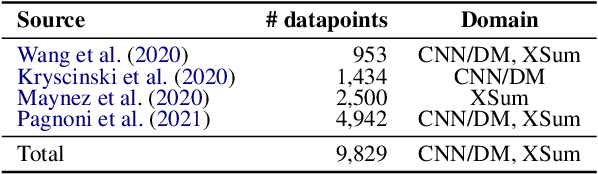
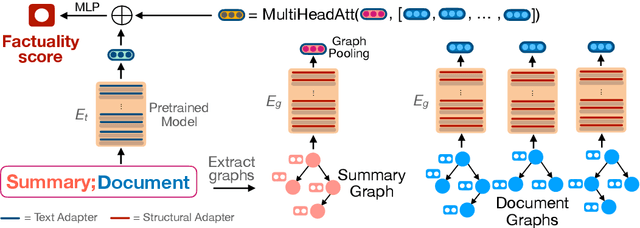
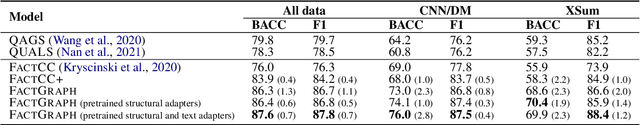
Despite recent improvements in abstractive summarization, most current approaches generate summaries that are not factually consistent with the source document, severely restricting their trust and usage in real-world applications. Recent works have shown promising improvements in factuality error identification using text or dependency arc entailments; however, they do not consider the entire semantic graph simultaneously. To this end, we propose FactGraph, a method that decomposes the document and the summary into structured meaning representations (MR), which are more suitable for factuality evaluation. MRs describe core semantic concepts and their relations, aggregating the main content in both document and summary in a canonical form, and reducing data sparsity. FactGraph encodes such graphs using a graph encoder augmented with structure-aware adapters to capture interactions among the concepts based on the graph connectivity, along with text representations using an adapter-based text encoder. Experiments on different benchmarks for evaluating factuality show that FactGraph outperforms previous approaches by up to 15%. Furthermore, FactGraph improves performance on identifying content verifiability errors and better captures subsentence-level factual inconsistencies.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge