Extracting evidence of supplement-drug interactions from literature
Paper and Code
Sep 17, 2019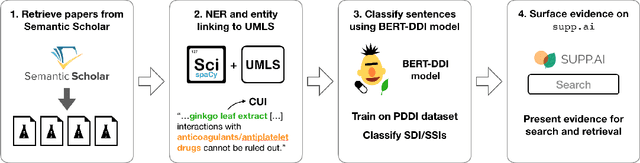
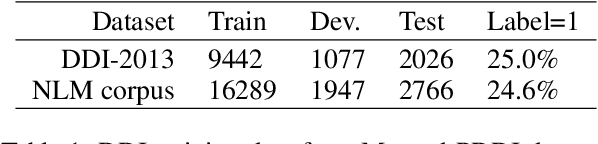
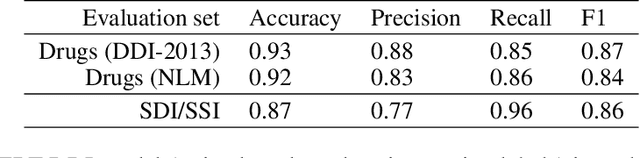
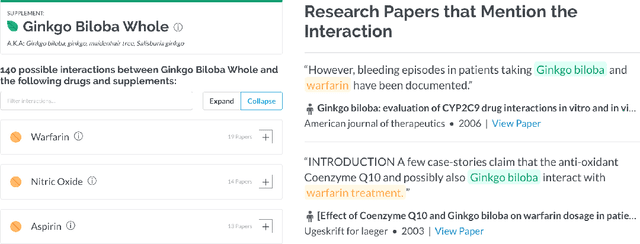
Dietary supplements are used by a large portion of the population, but information on their safety is hard to find. We demonstrate an automated method for extracting evidence of supplement-drug interactions (SDIs) and supplement-supplement interactions (SSIs) from scientific text. To address the lack of labeled data in this domain, we use labels of the closely related task of identifying drug-drug interactions (DDIs) for supervision, and assess the feasibility of transferring the model to identify supplement interactions. We fine-tune the contextualized word representations of BERT-large using labeled data from the PDDI corpus. We then process 22M abstracts from PubMed using this model, and extract evidence for 55946 unique interactions between 1923 supplements and 2727 drugs (precision: 0.77, recall: 0.96), demonstrating that learning the task of DDI classification transfers successfully to the related problem of identifying SDIs and SSIs. As far as we know, this is the first published work on detecting evidence of SDIs/SSIs from literature. We implement a freely-available public interface supp.ai to browse and search evidence sentences extracted by our model.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge