Exploring the Benefits of Domain-Pretraining of Generative Large Language Models for Chemistry
Paper and Code
Nov 05, 2024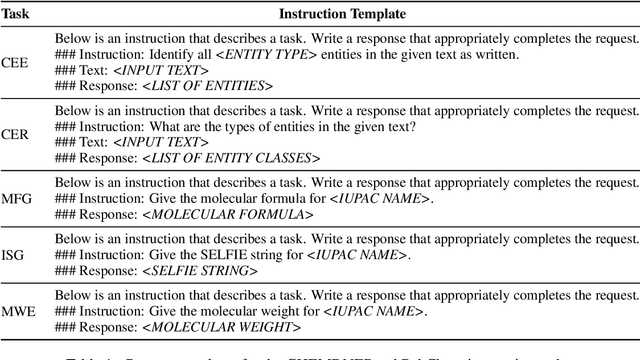
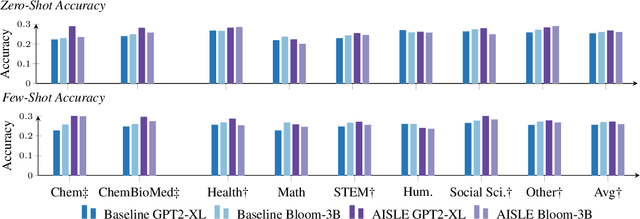
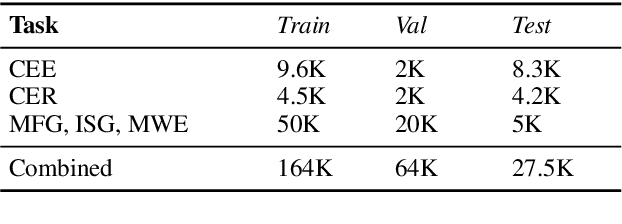
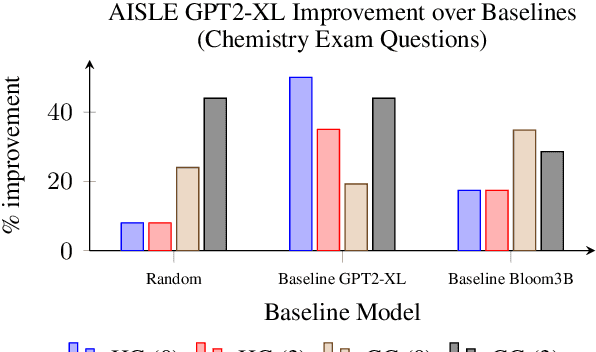
A proliferation of Large Language Models (the GPT series, BLOOM, LLaMA, and more) are driving forward novel development of multipurpose AI for a variety of tasks, particularly natural language processing (NLP) tasks. These models demonstrate strong performance on a range of tasks; however, there has been evidence of brittleness when applied to more niche or narrow domains where hallucinations or fluent but incorrect responses reduce performance. Given the complex nature of scientific domains, it is prudent to investigate the trade-offs of leveraging off-the-shelf versus more targeted foundation models for scientific domains. In this work, we examine the benefits of in-domain pre-training for a given scientific domain, chemistry, and compare these to open-source, off-the-shelf models with zero-shot and few-shot prompting. Our results show that not only do in-domain base models perform reasonably well on in-domain tasks in a zero-shot setting but that further adaptation using instruction fine-tuning yields impressive performance on chemistry-specific tasks such as named entity recognition and molecular formula generation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge