Explanation Shift: Investigating Interactions between Models and Shifting Data Distributions
Paper and Code
Mar 14, 2023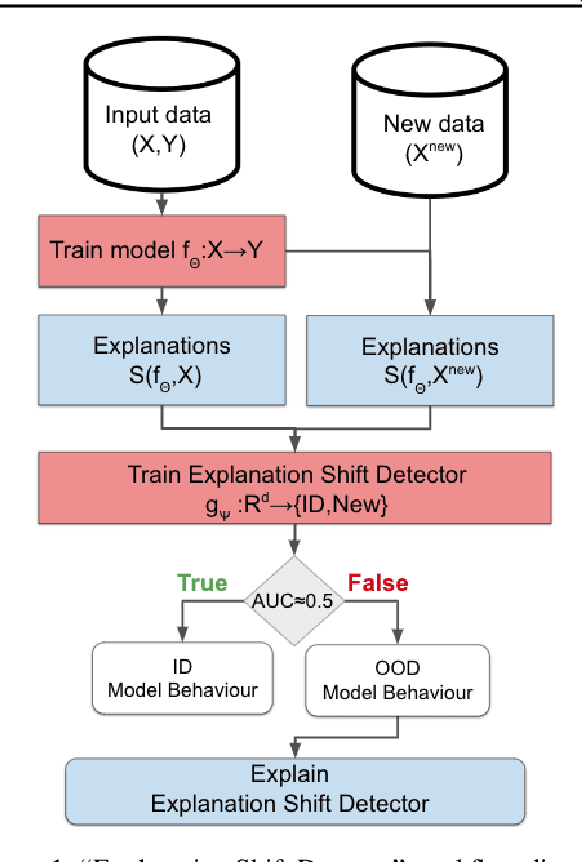
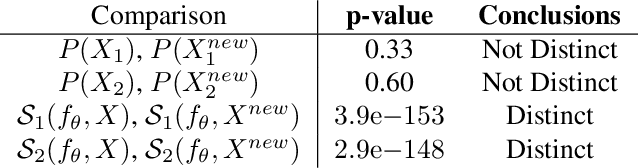
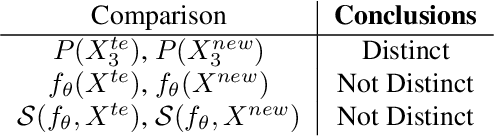
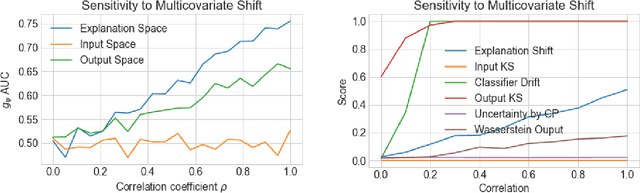
As input data distributions evolve, the predictive performance of machine learning models tends to deteriorate. In practice, new input data tend to come without target labels. Then, state-of-the-art techniques model input data distributions or model prediction distributions and try to understand issues regarding the interactions between learned models and shifting distributions. We suggest a novel approach that models how explanation characteristics shift when affected by distribution shifts. We find that the modeling of explanation shifts can be a better indicator for detecting out-of-distribution model behaviour than state-of-the-art techniques. We analyze different types of distribution shifts using synthetic examples and real-world data sets. We provide an algorithmic method that allows us to inspect the interaction between data set features and learned models and compare them to the state-of-the-art. We release our methods in an open-source Python package, as well as the code used to reproduce our experiments.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge