Event Data Association via Robust Model Fitting for Event-based Object Tracking
Paper and Code
Oct 25, 2021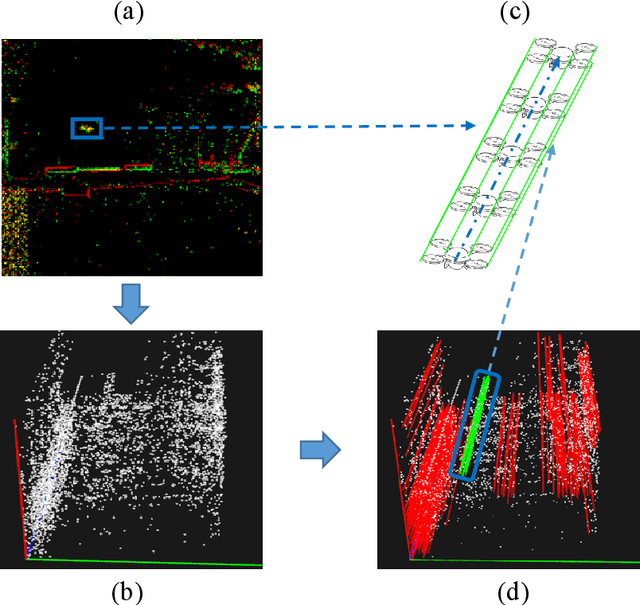
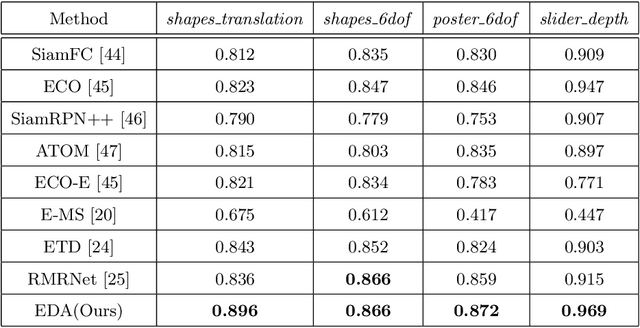
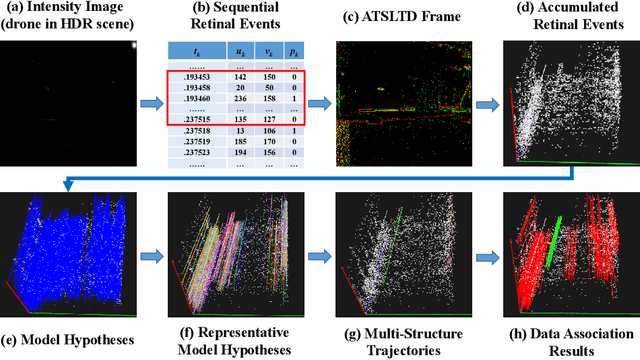
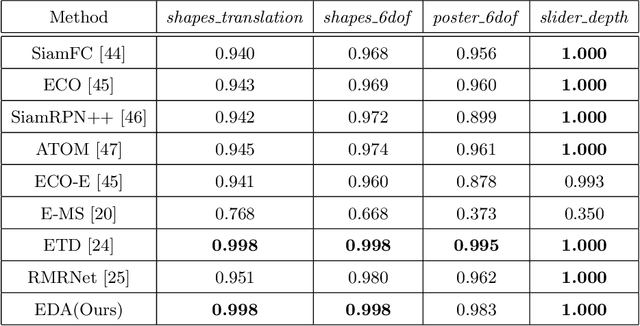
Event-based approaches, which are based on bio-inspired asynchronous event cameras, have achieved promising performance on various computer vision tasks. However, the study of the fundamental event data association problem is still in its infancy. In this paper, we propose a novel Event Data Association approach (called EDA) to explicitly address the data association problem. The proposed EDA seeks for event trajectories that best fit the event data, in order to perform unifying data association. In EDA, we first asynchronously gather the event data, based on its information entropy. Then, we introduce a deterministic model hypothesis generation strategy, which effectively generates model hypotheses from the gathered events, to represent the corresponding event trajectories. After that, we present a two-stage weighting algorithm, which robustly weighs and selects true models from the generated model hypotheses, through multi-structural geometric model fitting. Meanwhile, we also propose an adaptive model selection strategy to automatically determine the number of the true models. Finally, we use the selected true models to associate the event data, without being affected by sensor noise and irrelevant structures. We evaluate the performance of the proposed EDA on the object tracking task. The experimental results show the effectiveness of EDA under challenging scenarios, such as high speed, motion blur, and high dynamic range conditions.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge