Evaluating Privacy-Preserving Machine Learning in Critical Infrastructures: A Case Study on Time-Series Classification
Paper and Code
Nov 29, 2021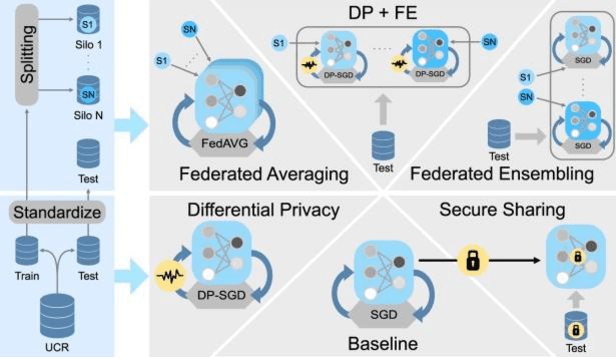
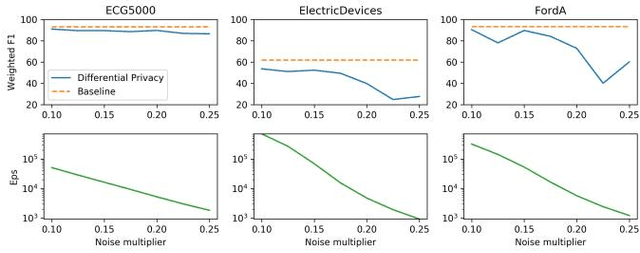
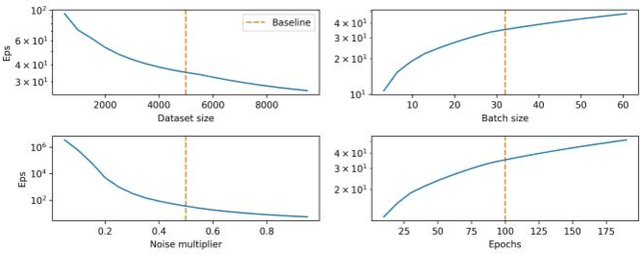
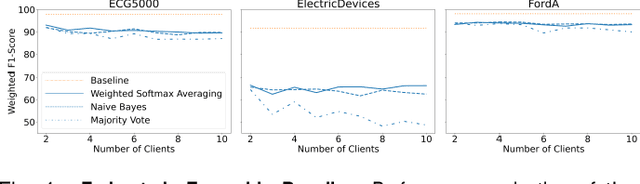
With the advent of machine learning in applications of critical infrastructure such as healthcare and energy, privacy is a growing concern in the minds of stakeholders. It is pivotal to ensure that neither the model nor the data can be used to extract sensitive information used by attackers against individuals or to harm whole societies through the exploitation of critical infrastructure. The applicability of machine learning in these domains is mostly limited due to a lack of trust regarding the transparency and the privacy constraints. Various safety-critical use cases (mostly relying on time-series data) are currently underrepresented in privacy-related considerations. By evaluating several privacy-preserving methods regarding their applicability on time-series data, we validated the inefficacy of encryption for deep learning, the strong dataset dependence of differential privacy, and the broad applicability of federated methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge