Evaluating Agent-based Program Repair at Google
Paper and Code
Jan 13, 2025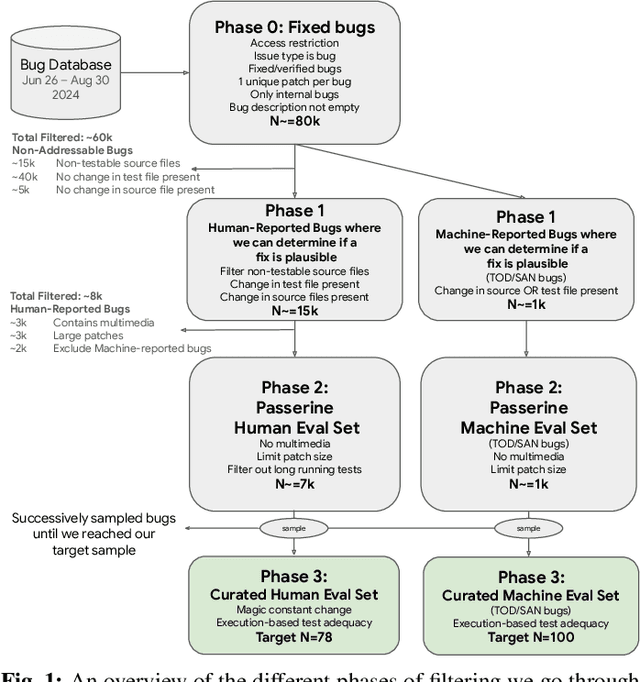
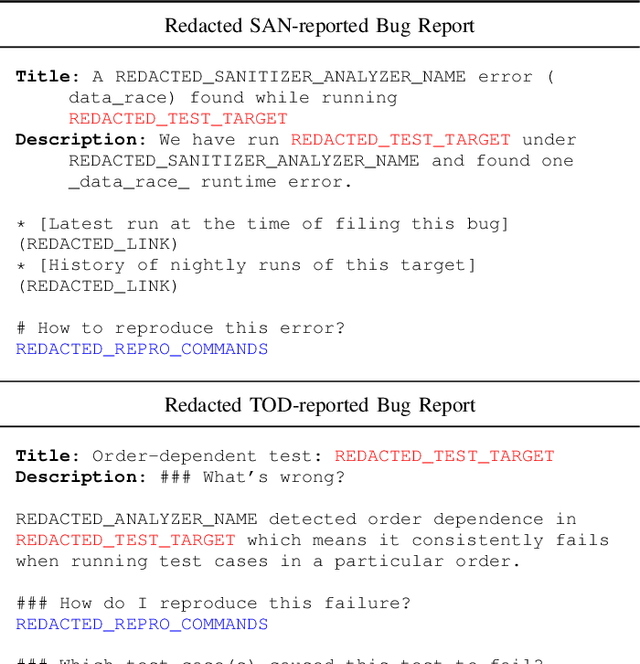
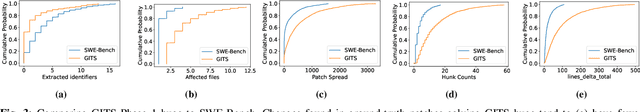
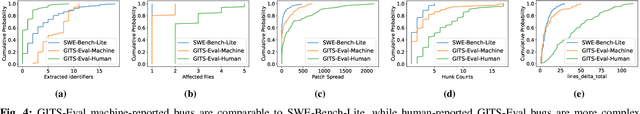
Agent-based program repair offers to automatically resolve complex bugs end-to-end by combining the planning, tool use, and code generation abilities of modern LLMs. Recent work has explored the use of agent-based repair approaches on the popular open-source SWE-Bench, a collection of bugs from highly-rated GitHub Python projects. In addition, various agentic approaches such as SWE-Agent have been proposed to solve bugs in this benchmark. This paper explores the viability of using an agentic approach to address bugs in an enterprise context. To investigate this, we curate an evaluation set of 178 bugs drawn from Google's issue tracking system. This dataset spans both human-reported (78) and machine-reported bugs (100). To establish a repair performance baseline on this benchmark, we implement Passerine, an agent similar in spirit to SWE-Agent that can work within Google's development environment. We show that with 20 trajectory samples and Gemini 1.5 Pro, Passerine can produce a patch that passes bug tests (i.e., plausible) for 73% of machine-reported and 25.6% of human-reported bugs in our evaluation set. After manual examination, we found that 43% of machine-reported bugs and 17.9% of human-reported bugs have at least one patch that is semantically equivalent to the ground-truth patch. These results establish a baseline on an industrially relevant benchmark, which as we show, contains bugs drawn from a different distribution -- in terms of language diversity, size, and spread of changes, etc. -- compared to those in the popular SWE-Bench dataset.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge