Ensemble Neural Representation Networks
Paper and Code
Oct 07, 2021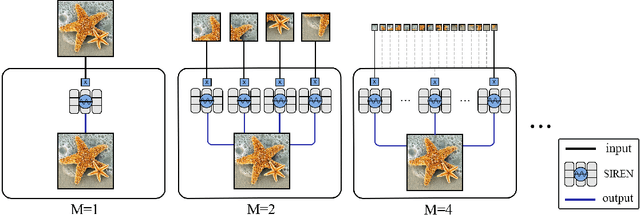

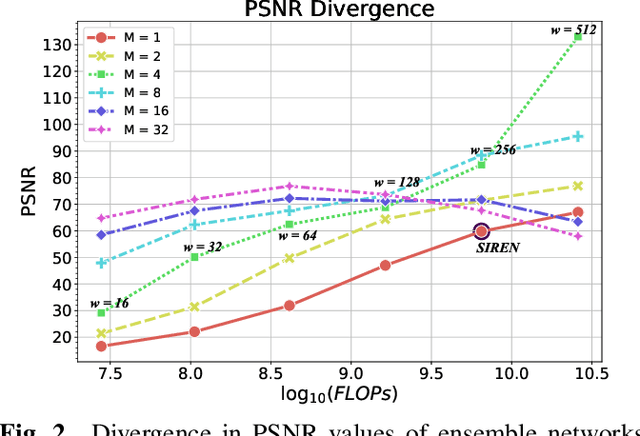

Implicit Neural Representation (INR) has recently attracted considerable attention for storing various types of signals in continuous forms. The existing INR networks require lengthy training processes and high-performance computational resources. In this paper, we propose a novel sub-optimal ensemble architecture for INR that resolves the aforementioned problems. In this architecture, the representation task is divided into several sub-tasks done by independent sub-networks. We show that the performance of the proposed ensemble INR architecture may decrease if the dimensions of sub-networks increase. Hence, it is vital to suggest an optimization algorithm to find the sub-optimal structure of the ensemble network, which is done in this paper. According to the simulation results, the proposed architecture not only has significantly fewer floating-point operations (FLOPs) and less training time, but it also has better performance in terms of Peak Signal to Noise Ratio (PSNR) compared to those of its counterparts.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge