Empowering parameter-efficient transfer learning by recognizing the kernel structure in self-attention
Paper and Code
May 07, 2022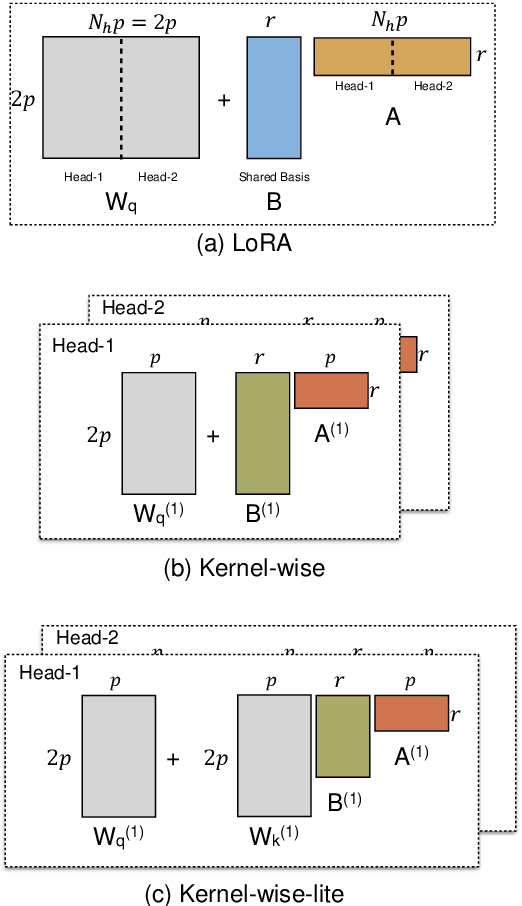
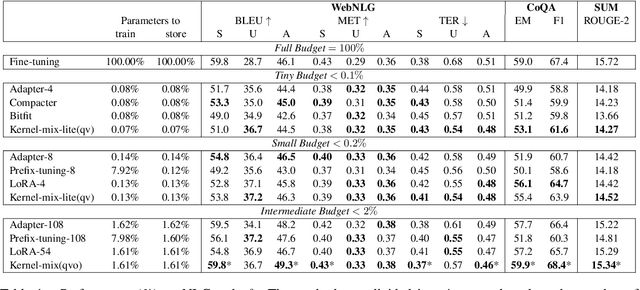
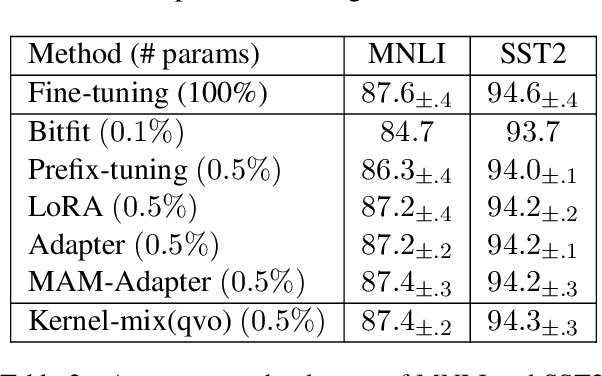
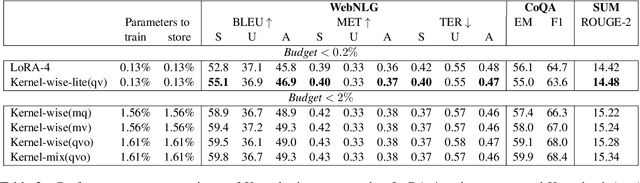
The massive amount of trainable parameters in the pre-trained language models (PLMs) makes them hard to be deployed to multiple downstream tasks. To address this issue, parameter-efficient transfer learning methods have been proposed to tune only a few parameters during fine-tuning while freezing the rest. This paper looks at existing methods along this line through the \textit{kernel lens}. Motivated by the connection between self-attention in transformer-based PLMs and kernel learning, we propose \textit{kernel-wise adapters}, namely \textit{Kernel-mix}, that utilize the kernel structure in self-attention to guide the assignment of the tunable parameters. These adapters use guidelines found in classical kernel learning and enable separate parameter tuning for each attention head. Our empirical results, over a diverse set of natural language generation and understanding tasks, show that our proposed adapters can attain or improve the strong performance of existing baselines.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge