Effective Fusion of Deep Multitasking Representations for Robust Visual Tracking
Paper and Code
Apr 03, 2020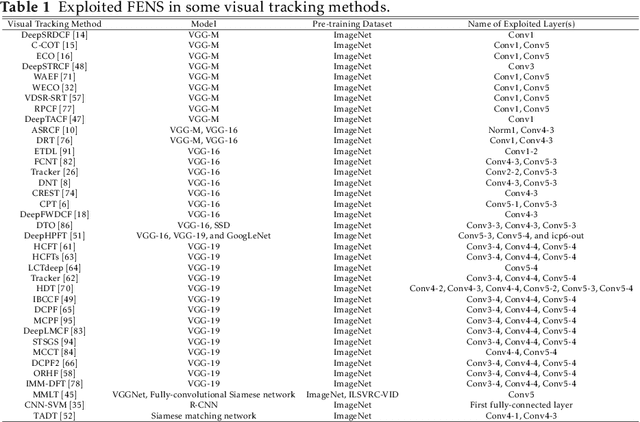
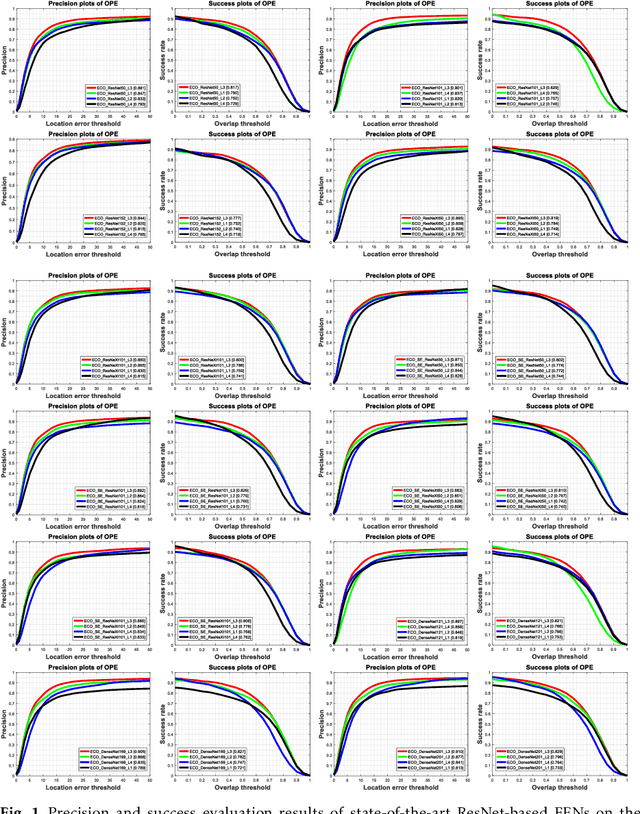
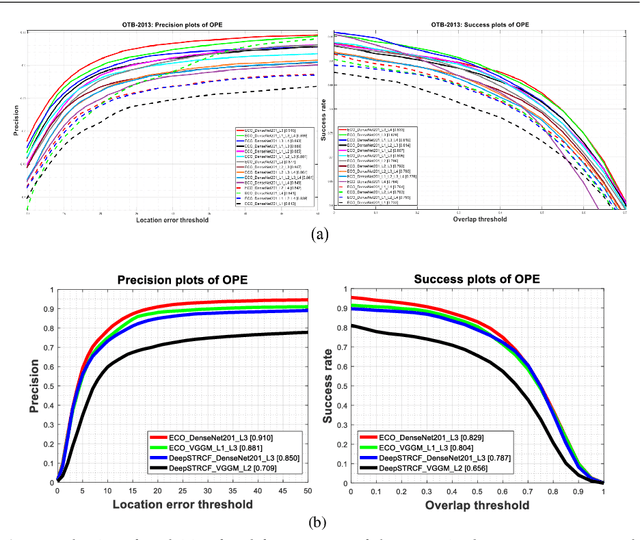
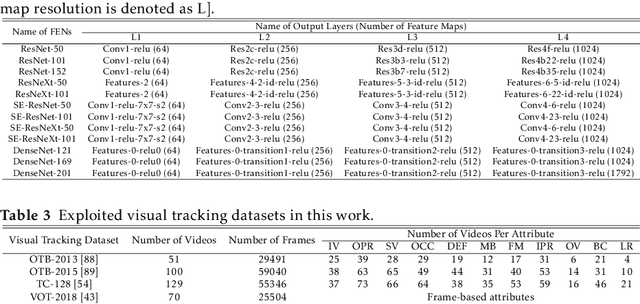
Visual object tracking remains an active research field in computer vision due to persisting challenges with various problem-specific factors in real-world scenes. Many existing tracking methods based on discriminative correlation filters (DCFs) employ feature extraction networks (FENs) to model the target appearance during the learning process. However, using deep feature maps extracted from FENs based on different residual neural networks (ResNets) has not previously been investigated. This paper aims to evaluate the performance of twelve state-of-the-art ResNet-based FENs in a DCF-based framework to determine the best for visual tracking purposes. First, it ranks their best feature maps and explores the generalized adoption of the best ResNet-based FEN into another DCF-based method. Then, the proposed method extracts deep semantic information from a fully convolutional FEN and fuses it with the best ResNet-based feature maps to strengthen the target representation in the learning process of continuous convolution filters. Finally, it introduces a new and efficient semantic weighting method (using semantic segmentation feature maps on each video frame) to reduce the drift problem. Extensive experimental results on the well-known OTB-2013, OTB-2015, TC-128 and VOT-2018 visual tracking datasets demonstrate that the proposed method effectively outperforms state-of-the-art methods in terms of precision and robustness of visual tracking.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge