Domain Generalization -- A Causal Perspective
Paper and Code
Sep 30, 2022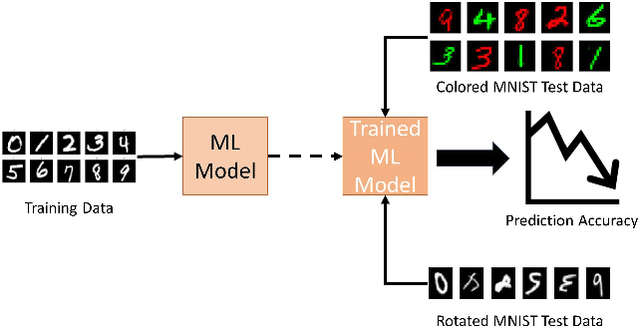
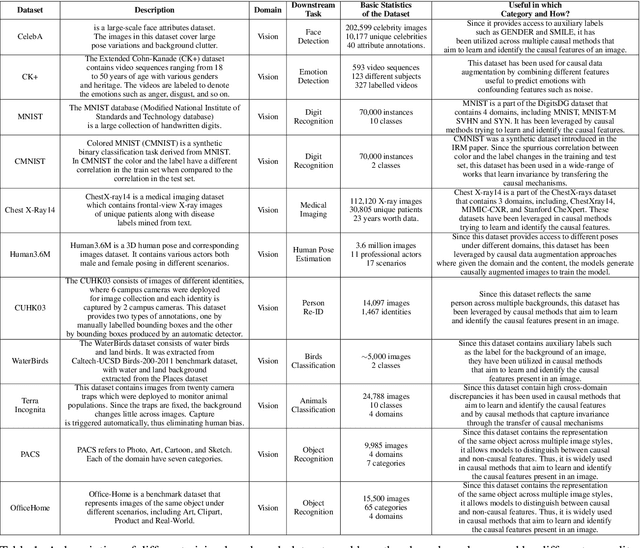
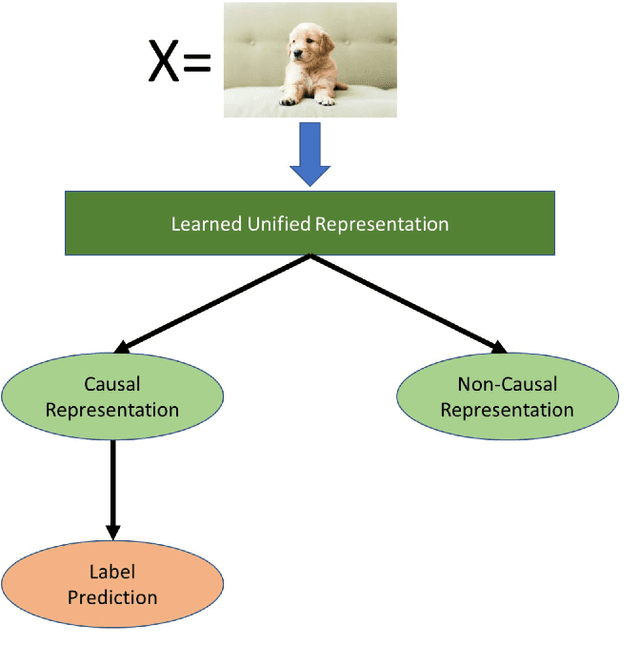
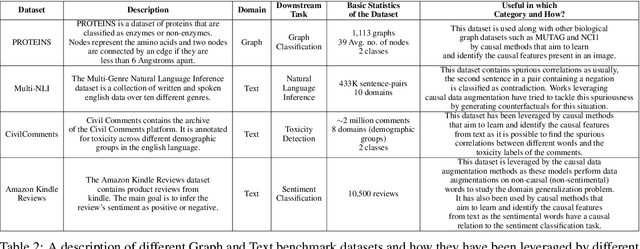
Machine learning models have gained widespread success, from healthcare to personalized recommendations. One of the preliminary assumptions of these models is the independent and identical distribution. Therefore, the train and test data are sampled from the same observation per this assumption. However, this assumption seldom holds in the real world due to distribution shifts. Since the models rely heavily on this assumption, they exhibit poor generalization capabilities. Over the recent years, dedicated efforts have been made to improve the generalization capabilities of these models. The primary idea behind these methods is to identify stable features or mechanisms that remain invariant across the different distributions. Many generalization approaches employ causal theories to describe invariance since causality and invariance are inextricably intertwined. However, current surveys deal with the causality-aware domain generalization methods on a very high-level. Furthermore, none of the existing surveys categorize the causal domain generalization methods based on the problem and causal theories these methods leverage. To this end, we present a comprehensive survey on causal domain generalization models from the aspects of the problem and causal theories. Furthermore, this survey includes in-depth insights into publicly accessible datasets and benchmarks for domain generalization in various domains. Finally, we conclude the survey with insights and discussions on future research directions. Finally, we conclude the survey with insights and discussions on future research directions.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge