DIVeR: Real-time and Accurate Neural Radiance Fields with Deterministic Integration for Volume Rendering
Paper and Code
Nov 19, 2021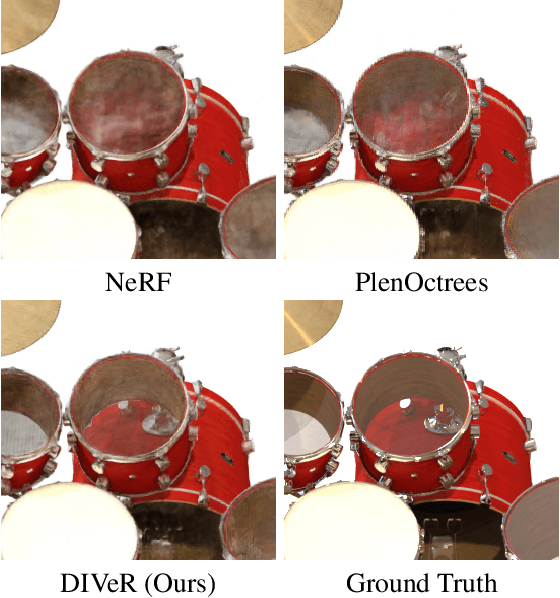
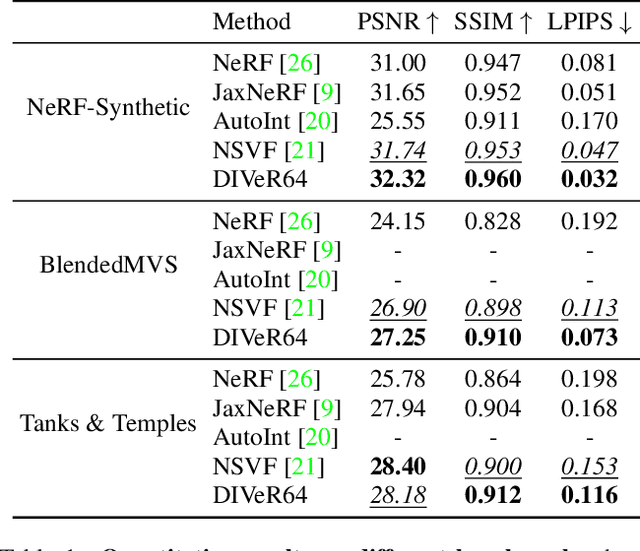
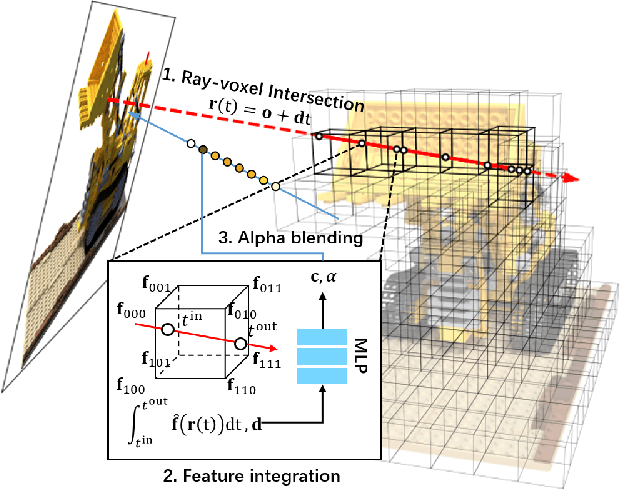
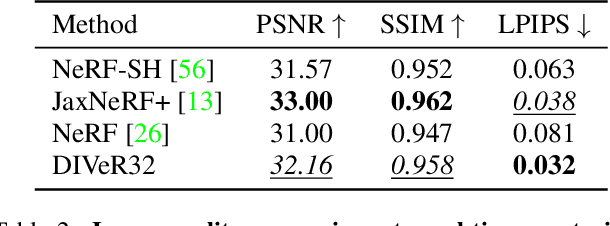
DIVeR builds on the key ideas of NeRF and its variants -- density models and volume rendering -- to learn 3D object models that can be rendered realistically from small numbers of images. In contrast to all previous NeRF methods, DIVeR uses deterministic rather than stochastic estimates of the volume rendering integral. DIVeR's representation is a voxel based field of features. To compute the volume rendering integral, a ray is broken into intervals, one per voxel; components of the volume rendering integral are estimated from the features for each interval using an MLP, and the components are aggregated. As a result, DIVeR can render thin translucent structures that are missed by other integrators. Furthermore, DIVeR's representation has semantics that is relatively exposed compared to other such methods -- moving feature vectors around in the voxel space results in natural edits. Extensive qualitative and quantitative comparisons to current state-of-the-art methods show that DIVeR produces models that (1) render at or above state-of-the-art quality, (2) are very small without being baked, (3) render very fast without being baked, and (4) can be edited in natural ways.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge