Disentangled dimensionality reduction for noise-robust speaker diarisation
Paper and Code
Oct 07, 2021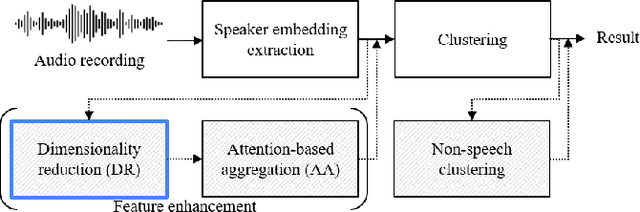
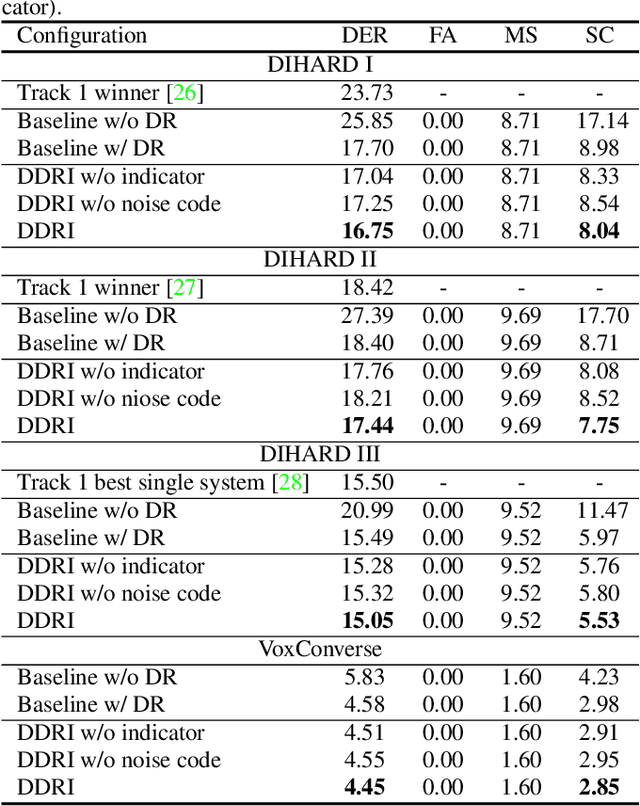
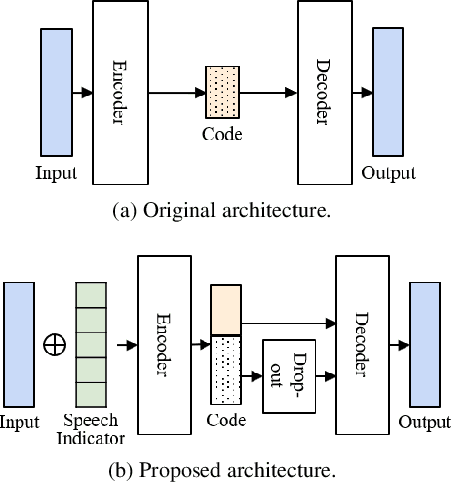

The objective of this work is to train noise-robust speaker embeddings for speaker diarisation. Speaker embeddings play a crucial role in the performance of diarisation systems, but they often capture spurious information such as noise and reverberation, adversely affecting performance. Our previous work have proposed an auto-encoder-based dimensionality reduction module to help remove the spurious information. However, they do not explicitly separate such information and have also been found to be sensitive to hyperparameter values. To this end, we propose two contributions to overcome these issues: (i) a novel dimensionality reduction framework that can disentangle spurious information from the speaker embeddings; (ii) the use of a speech/non-speech indicator to prevent the speaker code from learning from the background noise. Through a range of experiments conducted on four different datasets, our approach consistently demonstrates the state-of-the-art performance among models that do not adopt ensembles.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge