Discerning and Enhancing the Weighted Sum-Rate Maximization Algorithms in Communications
Paper and Code
Nov 08, 2023
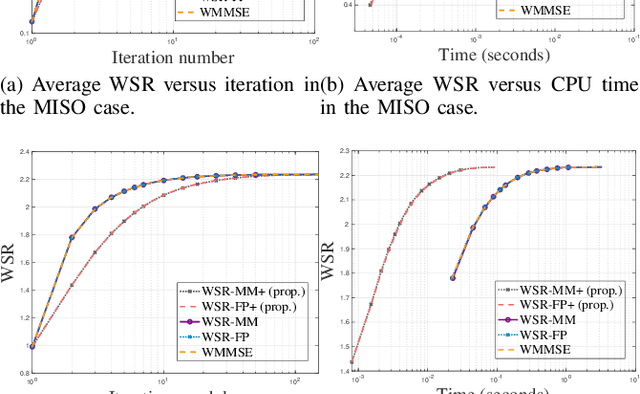
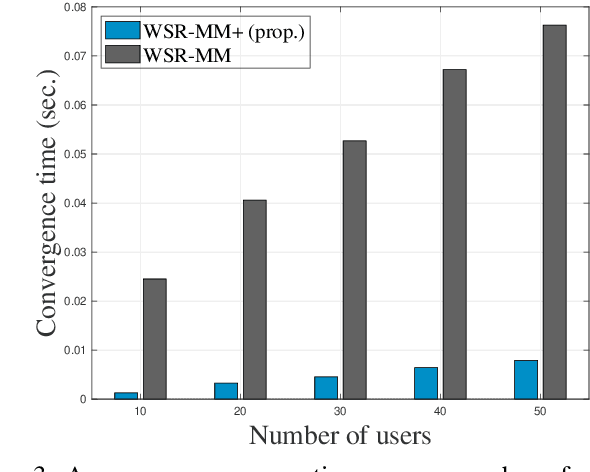
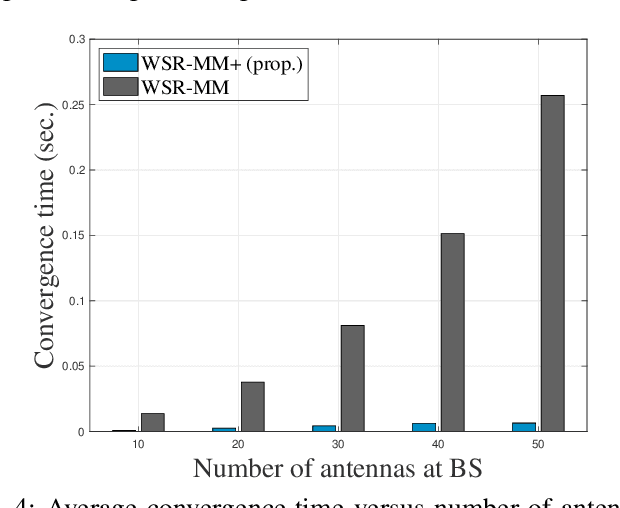
Weighted sum-rate (WSR) maximization plays a critical role in communication system design. This paper examines three optimization methods for WSR maximization, which ensure convergence to stationary points: two block coordinate ascent (BCA) algorithms, namely, weighted sum-minimum mean-square error (WMMSE) and WSR maximization via fractional programming (WSR-FP), along with a minorization-maximization (MM) algorithm, WSR maximization via MM (WSR-MM). Our contributions are threefold. Firstly, we delineate the exact relationships among WMMSE, WSR-FP, and WSR-MM, which, despite their extensive use in the literature, lack a comprehensive comparative study. By probing the theoretical underpinnings linking the BCA and MM algorithmic frameworks, we reveal the direct correlations between the equivalent transformation techniques, essential to the development of WMMSE and WSR-FP, and the surrogate functions pivotal to WSR-MM. Secondly, we propose a novel algorithm, WSR-MM+, harnessing the flexibility of selecting surrogate functions in MM framework. By circumventing the repeated matrix inversions in the search for optimal Lagrange multipliers in existing algorithms, WSR-MM+ significantly reduces the computational load per iteration and accelerates convergence. Thirdly, we reconceptualize WSR-MM+ within the BCA framework, introducing a new equivalent transform, which gives rise to an enhanced version of WSR-FP, named as WSR-FP+. We further demonstrate that WSR-MM+ can be construed as the basic gradient projection method. This perspective yields a deeper understanding into its computational intricacies. Numerical simulations corroborate the connections between WMMSE, WSR-FP, and WSR-MM and confirm the efficacy of the proposed WSR-MM+ and WSR-FP+ algorithms.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge