DiffusionBlend: Learning 3D Image Prior through Position-aware Diffusion Score Blending for 3D Computed Tomography Reconstruction
Paper and Code
Jun 14, 2024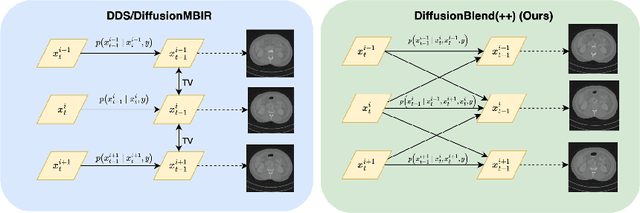
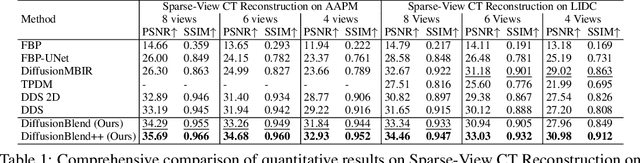
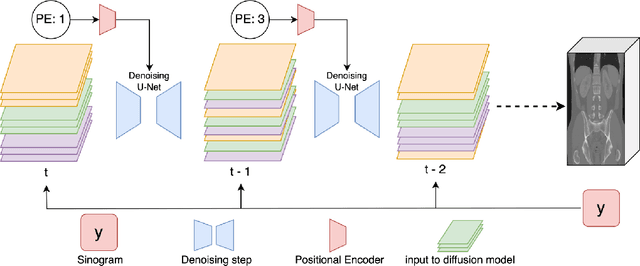
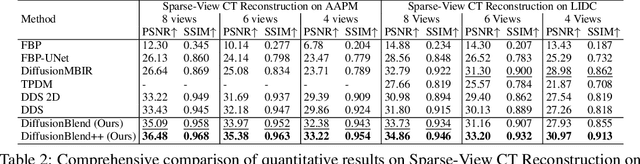
Diffusion models face significant challenges when employed for large-scale medical image reconstruction in real practice such as 3D Computed Tomography (CT). Due to the demanding memory, time, and data requirements, it is difficult to train a diffusion model directly on the entire volume of high-dimensional data to obtain an efficient 3D diffusion prior. Existing works utilizing diffusion priors on single 2D image slice with hand-crafted cross-slice regularization would sacrifice the z-axis consistency, which results in severe artifacts along the z-axis. In this work, we propose a novel framework that enables learning the 3D image prior through position-aware 3D-patch diffusion score blending for reconstructing large-scale 3D medical images. To the best of our knowledge, we are the first to utilize a 3D-patch diffusion prior for 3D medical image reconstruction. Extensive experiments on sparse view and limited angle CT reconstruction show that our DiffusionBlend method significantly outperforms previous methods and achieves state-of-the-art performance on real-world CT reconstruction problems with high-dimensional 3D image (i.e., $256 \times 256 \times 500$). Our algorithm also comes with better or comparable computational efficiency than previous state-of-the-art methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge