DictBERT: Dictionary Description Knowledge Enhanced Language Model Pre-training via Contrastive Learning
Paper and Code
Aug 01, 2022
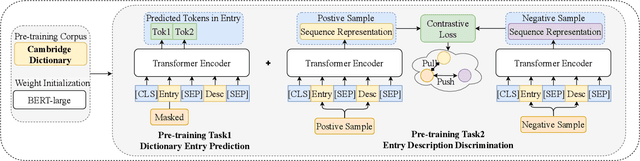

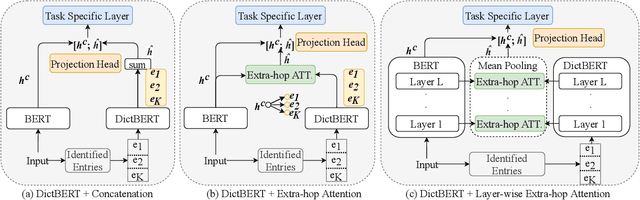
Although pre-trained language models (PLMs) have achieved state-of-the-art performance on various natural language processing (NLP) tasks, they are shown to be lacking in knowledge when dealing with knowledge driven tasks. Despite the many efforts made for injecting knowledge into PLMs, this problem remains open. To address the challenge, we propose \textbf{DictBERT}, a novel approach that enhances PLMs with dictionary knowledge which is easier to acquire than knowledge graph (KG). During pre-training, we present two novel pre-training tasks to inject dictionary knowledge into PLMs via contrastive learning: \textit{dictionary entry prediction} and \textit{entry description discrimination}. In fine-tuning, we use the pre-trained DictBERT as a plugin knowledge base (KB) to retrieve implicit knowledge for identified entries in an input sequence, and infuse the retrieved knowledge into the input to enhance its representation via a novel extra-hop attention mechanism. We evaluate our approach on a variety of knowledge driven and language understanding tasks, including NER, relation extraction, CommonsenseQA, OpenBookQA and GLUE. Experimental results demonstrate that our model can significantly improve typical PLMs: it gains a substantial improvement of 0.5\%, 2.9\%, 9.0\%, 7.1\% and 3.3\% on BERT-large respectively, and is also effective on RoBERTa-large.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge