DefGoalNet: Contextual Goal Learning from Demonstrations For Deformable Object Manipulation
Paper and Code
Sep 25, 2023

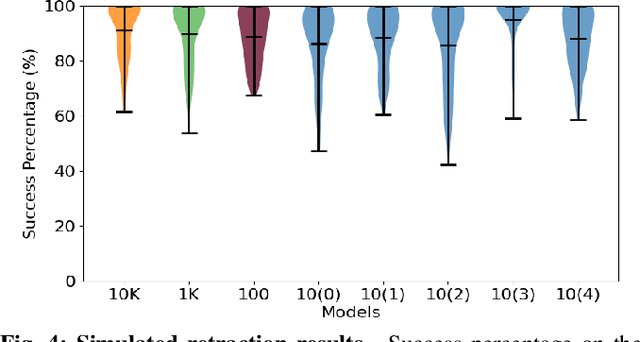

Shape servoing, a robotic task dedicated to controlling objects to desired goal shapes, is a promising approach to deformable object manipulation. An issue arises, however, with the reliance on the specification of a goal shape. This goal has been obtained either by a laborious domain knowledge engineering process or by manually manipulating the object into the desired shape and capturing the goal shape at that specific moment, both of which are impractical in various robotic applications. In this paper, we solve this problem by developing a novel neural network DefGoalNet, which learns deformable object goal shapes directly from a small number of human demonstrations. We demonstrate our method's effectiveness on various robotic tasks, both in simulation and on a physical robot. Notably, in the surgical retraction task, even when trained with as few as 10 demonstrations, our method achieves a median success percentage of nearly 90%. These results mark a substantial advancement in enabling shape servoing methods to bring deformable object manipulation closer to practical, real-world applications.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge