Deep Variational Luenberger-type Observer for Stochastic Video Prediction
Paper and Code
Feb 12, 2020
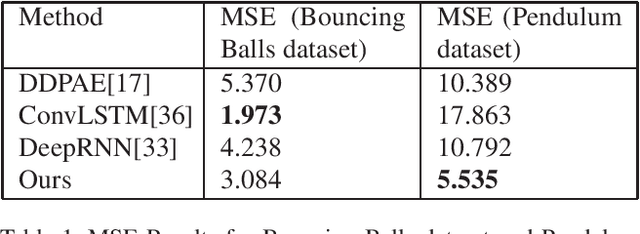


Considering the inherent stochasticity and uncertainty, predicting future video frames is exceptionally challenging. In this work, we study the problem of video prediction by combining interpretability of stochastic state space models and representation learning of deep neural networks. Our model builds upon an variational encoder which transforms the input video into a latent feature space and a Luenberger-type observer which captures the dynamic evolution of the latent features. This enables the decomposition of videos into static features and dynamics in an unsupervised manner. By deriving the stability theory of the nonlinear Luenberger-type observer, the hidden states in the feature space become insensitive with respect to the initial values, which improves the robustness of the overall model. Furthermore, the variational lower bound on the data log-likelihood can be derived to obtain the tractable posterior prediction distribution based on the variational principle. Finally, the experiments such as the Bouncing Balls dataset and the Pendulum dataset are provided to demonstrate the proposed model outperforms concurrent works.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge