Deep Learning Improves Template Matching by Normalized Cross Correlation
Paper and Code
May 24, 2017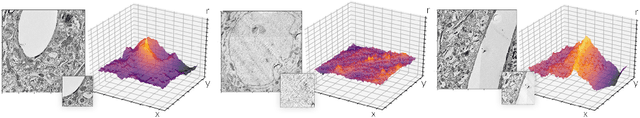

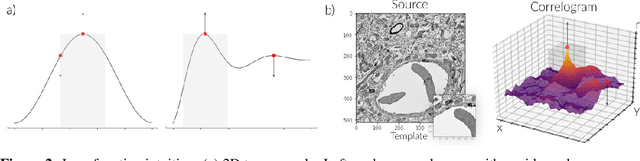
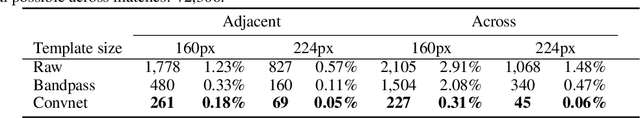
Template matching by normalized cross correlation (NCC) is widely used for finding image correspondences. We improve the robustness of this algorithm by preprocessing images with "siamese" convolutional networks trained to maximize the contrast between NCC values of true and false matches. The improvement is quantified using patches of brain images from serial section electron microscopy. Relative to a parameter-tuned bandpass filter, siamese convolutional networks significantly reduce false matches. Furthermore, all false matches can be eliminated by removing a tiny fraction of all matches based on NCC values. The improved accuracy of our method could be essential for connectomics, because emerging petascale datasets may require billions of template matches to assemble 2D images of serial sections into a 3D image stack. Our method is also expected to generalize to many other computer vision applications that use NCC template matching to find image correspondences.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge