Deep Equilibrium Models are Almost Equivalent to Not-so-deep Explicit Models for High-dimensional Gaussian Mixtures
Paper and Code
Feb 05, 2024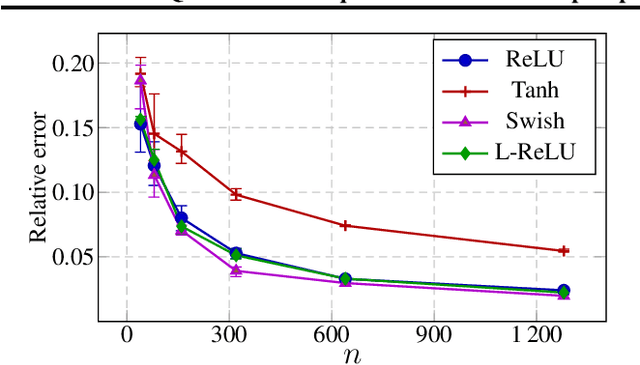
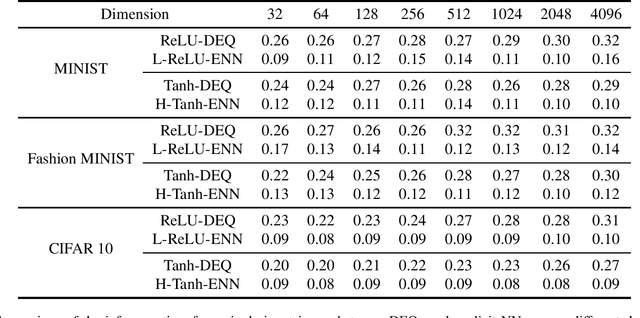
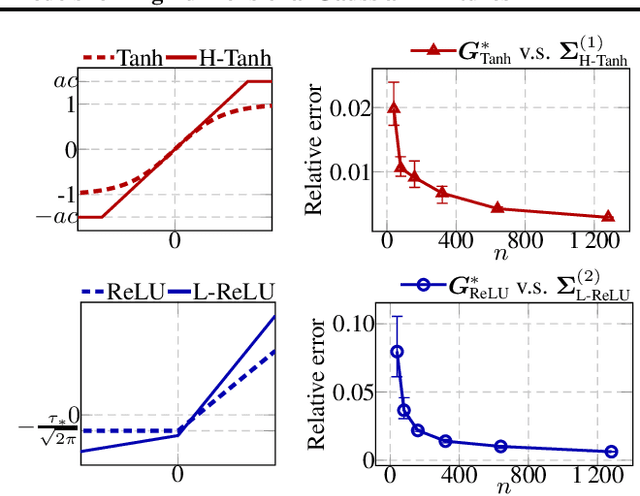
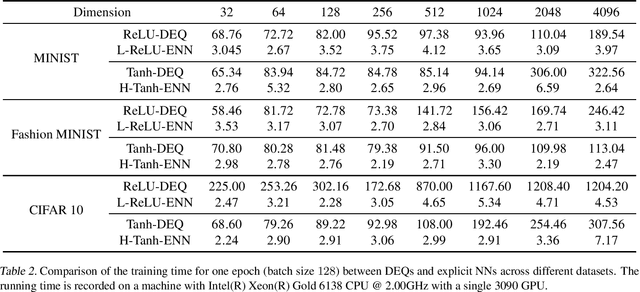
Deep equilibrium models (DEQs), as a typical implicit neural network, have demonstrated remarkable success on various tasks. There is, however, a lack of theoretical understanding of the connections and differences between implicit DEQs and explicit neural network models. In this paper, leveraging recent advances in random matrix theory (RMT), we perform an in-depth analysis on the eigenspectra of the conjugate kernel (CK) and neural tangent kernel (NTK) matrices for implicit DEQs, when the input data are drawn from a high-dimensional Gaussian mixture. We prove, in this setting, that the spectral behavior of these Implicit-CKs and NTKs depend on the DEQ activation function and initial weight variances, but only via a system of four nonlinear equations. As a direct consequence of this theoretical result, we demonstrate that a shallow explicit network can be carefully designed to produce the same CK or NTK as a given DEQ. Despite derived here for Gaussian mixture data, empirical results show the proposed theory and design principle also apply to popular real-world datasets.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge