Deep Air Learning: Interpolation, Prediction, and Feature Analysis of Fine-grained Air Quality
Paper and Code
Apr 11, 2018
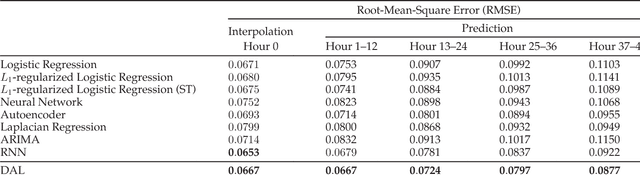
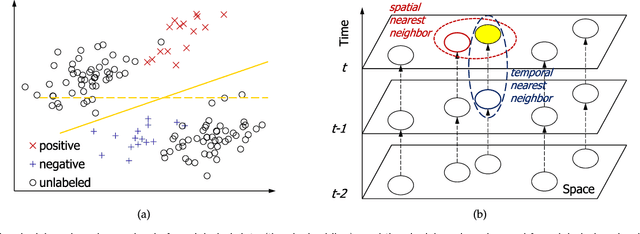

The interpolation, prediction, and feature analysis of fine-gained air quality are three important topics in the area of urban air computing. The solutions to these topics can provide extremely useful information to support air pollution control, and consequently generate great societal and technical impacts. Most of the existing work solves the three problems separately by different models. In this paper, we propose a general and effective approach to solve the three problems in one model called the Deep Air Learning (DAL). The main idea of DAL lies in embedding feature selection and semi-supervised learning in different layers of the deep learning network. The proposed approach utilizes the information pertaining to the unlabeled spatio-temporal data to improve the performance of the interpolation and the prediction, and performs feature selection and association analysis to reveal the main relevant features to the variation of the air quality. We evaluate our approach with extensive experiments based on real data sources obtained in Beijing, China. Experiments show that DAL is superior to the peer models from the recent literature when solving the topics of interpolation, prediction, and feature analysis of fine-gained air quality.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge