Deep 3D Vessel Segmentation based on Cross Transformer Network
Paper and Code
Aug 23, 2022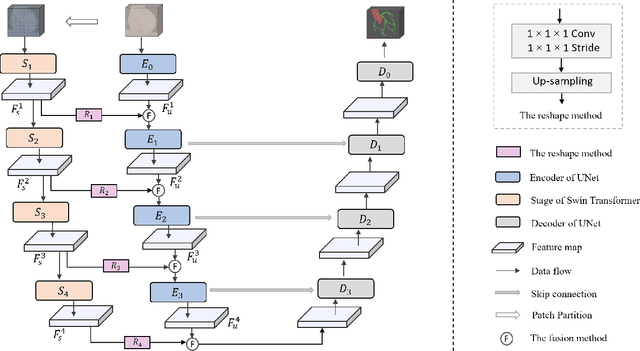
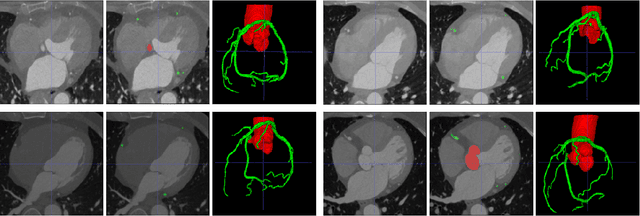
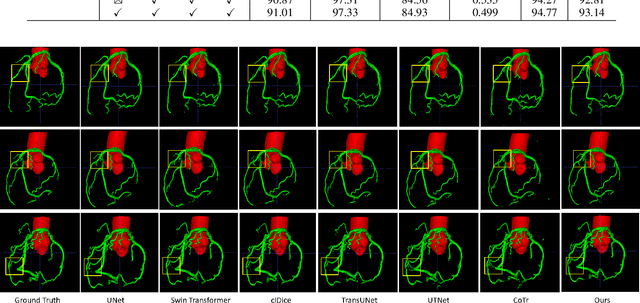
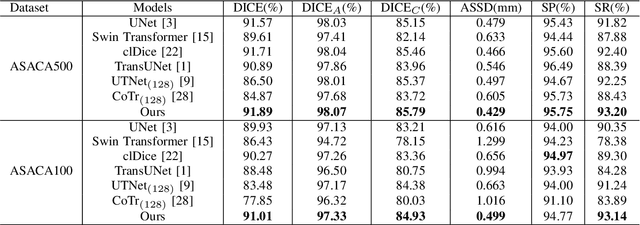
The coronary microvascular disease poses a great threat to human health. Computer-aided analysis/diagnosis systems help physicians intervene in the disease at early stages, where 3D vessel segmentation is a fundamental step. However, there is a lack of carefully annotated dataset to support algorithm development and evaluation. On the other hand, the commonly-used U-Net structures often yield disconnected and inaccurate segmentation results, especially for small vessel structures. In this paper, motivated by the data scarcity, we first construct two large-scale vessel segmentation datasets consisting of 100 and 500 computed tomography (CT) volumes with pixel-level annotations by experienced radiologists. To enhance the U-Net, we further propose the cross transformer network (CTN) for fine-grained vessel segmentation. In CTN, a transformer module is constructed in parallel to a U-Net to learn long-distance dependencies between different anatomical regions; and these dependencies are communicated to the U-Net at multiple stages to endow it with global awareness. Experimental results on the two in-house datasets indicate that this hybrid model alleviates unexpected disconnections by considering topological information across regions. Our codes, together with the trained models are made publicly available at https://github.com/qibaolian/ctn.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge