Decompositional Quantum Graph Neural Network
Paper and Code
Jan 13, 2022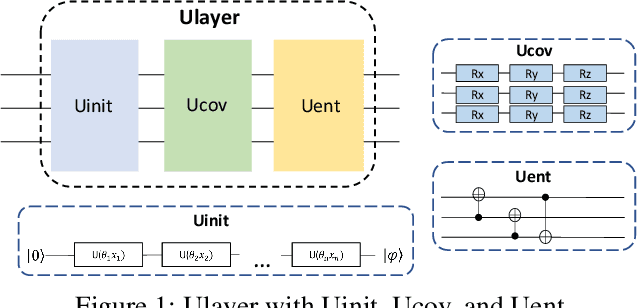
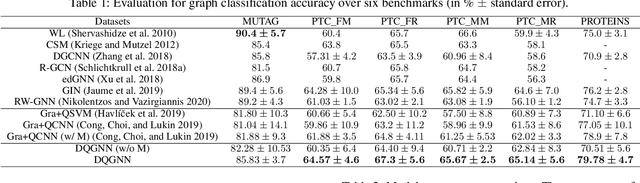
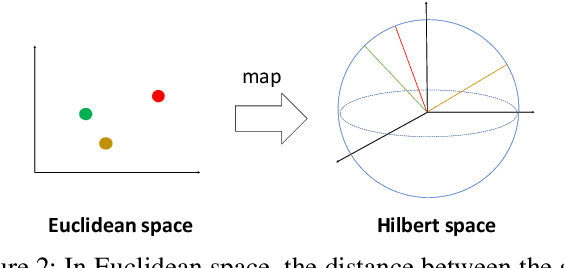
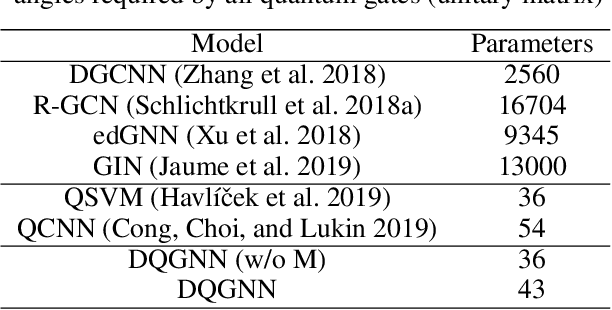
Quantum machine learning is a fast emerging field that aims to tackle machine learning using quantum algorithms and quantum computing. Due to the lack of physical qubits and an effective means to map real-world data from Euclidean space to Hilbert space, most of these methods focus on quantum analogies or process simulations rather than devising concrete architectures based on qubits. In this paper, we propose a novel hybrid quantum-classical algorithm for graph-structured data, which we refer to as the Decompositional Quantum Graph Neural Network (DQGNN). DQGNN implements the GNN theoretical framework using the tensor product and unity matrices representation, which greatly reduces the number of model parameters required. When controlled by a classical computer, DQGNN can accommodate arbitrarily sized graphs by processing substructures from the input graph using a modestly-sized quantum device. The architecture is based on a novel mapping from real-world data to Hilbert space. This mapping maintains the distance relations present in the data and reduces information loss. Experimental results show that the proposed method outperforms competitive state-of-the-art models with only 1.68\% parameters compared to those models.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge