DDNet: Cartesian-polar Dual-domain Network for the Joint Optic Disc and Cup Segmentation
Paper and Code
Apr 18, 2019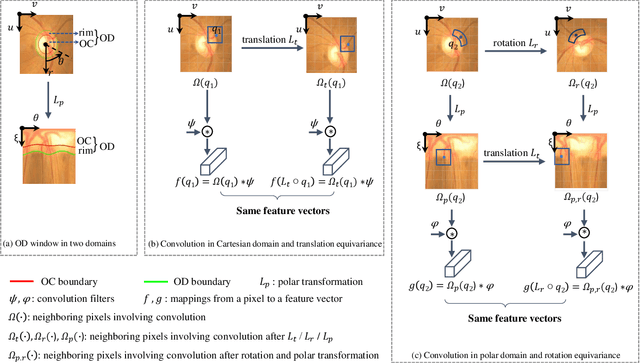


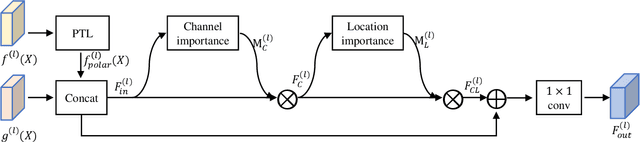
Existing joint optic disc and cup segmentation approaches are developed either in Cartesian or polar coordinate system. However, due to the subtle optic cup, the contextual information exploited from the single domain even by the prevailing CNNs is still insufficient. In this paper, we propose a novel segmentation approach, named Cartesian-polar dual-domain network (DDNet), which for the first time considers the complementary of the Cartesian domain and the polar domain. We propose a two-branch of domain feature encoder and learn translation equivariant representations on rectilinear grid from Cartesian domain and rotation equivariant representations on polar grid from polar domain parallelly. To fuse the features on two different grids, we propose a dual-domain fusion module. This module builds the correspondence between two grids by the differentiable polar transform layer and learns the feature importance across two domains in element-wise to enhance the expressive capability. Finally, the decoder aggregates the fused features from low-level to high-level and makes dense predictions. We validate the state-of-the-art segmentation performances of our DDNet on the public dataset ORIGA. According to the segmentation masks, we estimate the commonly used clinical measure for glaucoma, i.e., the vertical cup-to-disc ratio. The low cup-to-disc ratio estimation error demonstrates the potential application in glaucoma screening.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge