DASH: Visual Analytics for Debiasing Image Classification via User-Driven Synthetic Data Augmentation
Paper and Code
Sep 14, 2022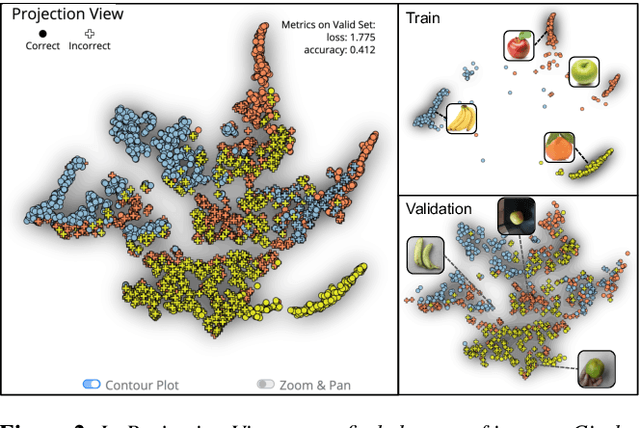
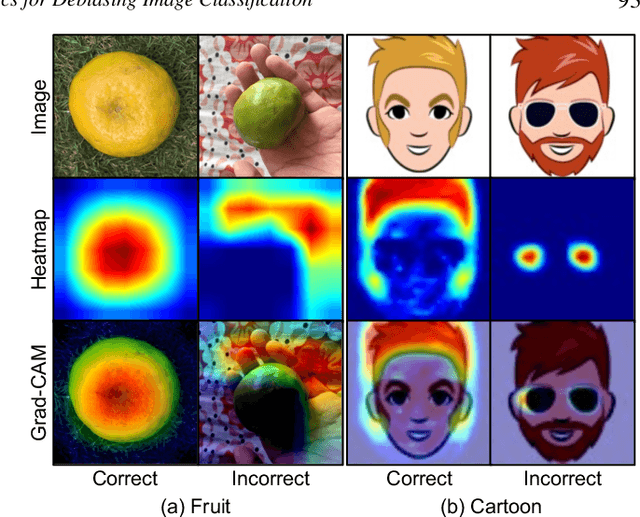
Image classification models often learn to predict a class based on irrelevant co-occurrences between input features and an output class in training data. We call the unwanted correlations "data biases," and the visual features causing data biases "bias factors." It is challenging to identify and mitigate biases automatically without human intervention. Therefore, we conducted a design study to find a human-in-the-loop solution. First, we identified user tasks that capture the bias mitigation process for image classification models with three experts. Then, to support the tasks, we developed a visual analytics system called DASH that allows users to visually identify bias factors, to iteratively generate synthetic images using a state-of-the-art image-to-image translation model, and to supervise the model training process for improving the classification accuracy. Our quantitative evaluation and qualitative study with ten participants demonstrate the usefulness of DASH and provide lessons for future work.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge