DACSR: Dual-Aggregation End-to-End Calibrated Sequential Recommendation
Paper and Code
Apr 29, 2022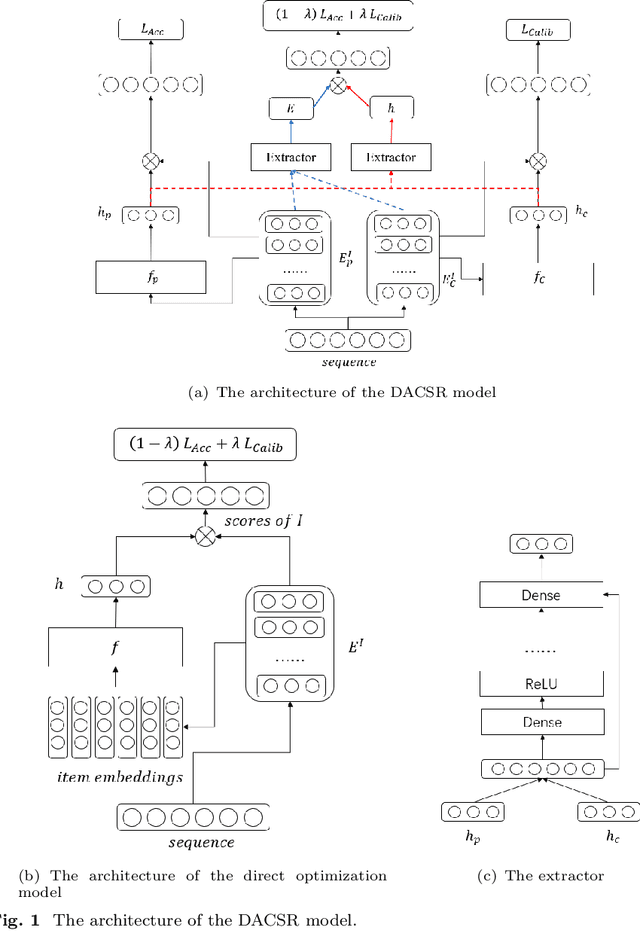

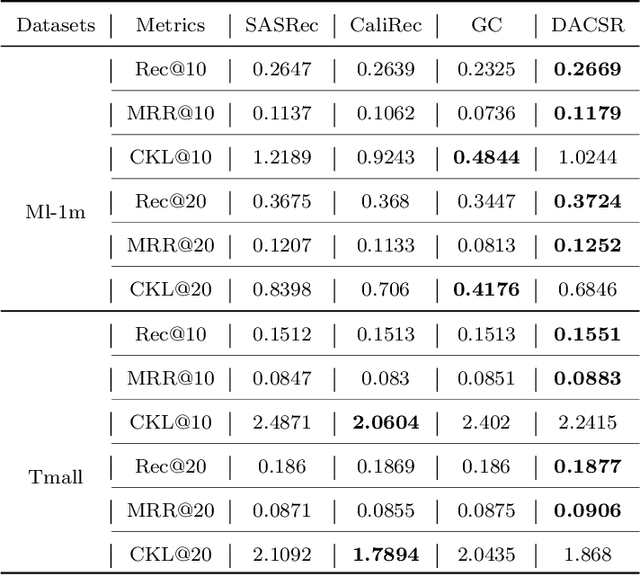
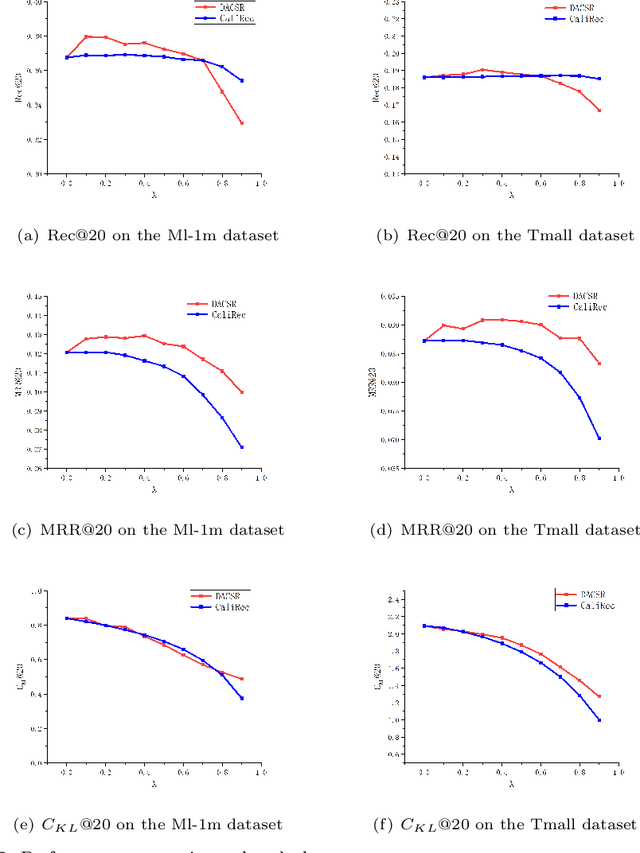
Recent years have witnessed the progress of sequential recommendation in accurately predicting users' future behaviors. However, only persuading accuracy leads to the risk of filter bubbles where recommenders only focus on users' main interest areas. Different from other studies which improve diversity or coverage, we investigate the calibration in sequential recommendation. However, existing calibrated methods followed a post-processing paradigm, which costs more computation time and sacrifices the recommendation accuracy. To this end, we propose an end-to-end framework to provide both accurate and calibrated recommendations. We propose a loss function to measure the divergence of distributions between recommendation lists and historical behaviors for sequential recommendation framework. In addition, we design a dual-aggregation model which extracts information from two individual sequence encoders with different objectives to further improve the recommendation. Experiments on two benchmark datasets demonstrate the effectiveness and efficiency of our model.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge