Cumulative Prospect Theory Meets Reinforcement Learning: Prediction and Control
Paper and Code
Feb 26, 2016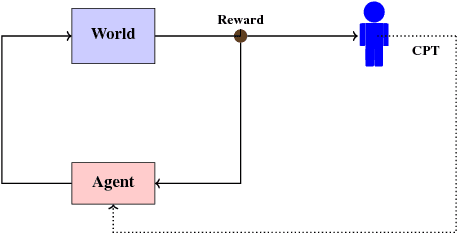
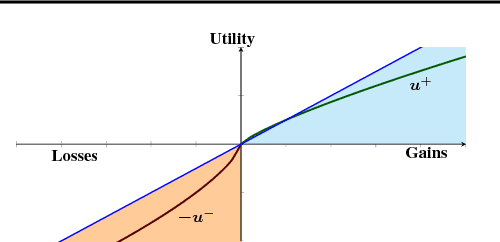
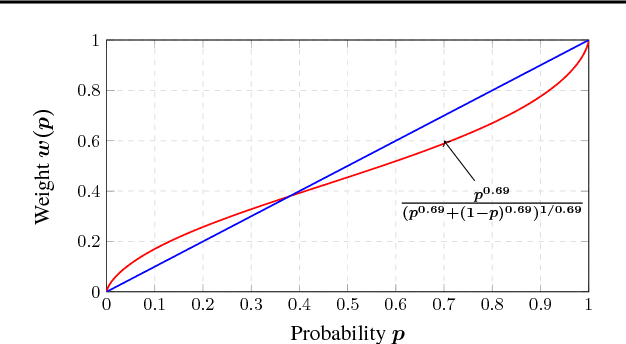
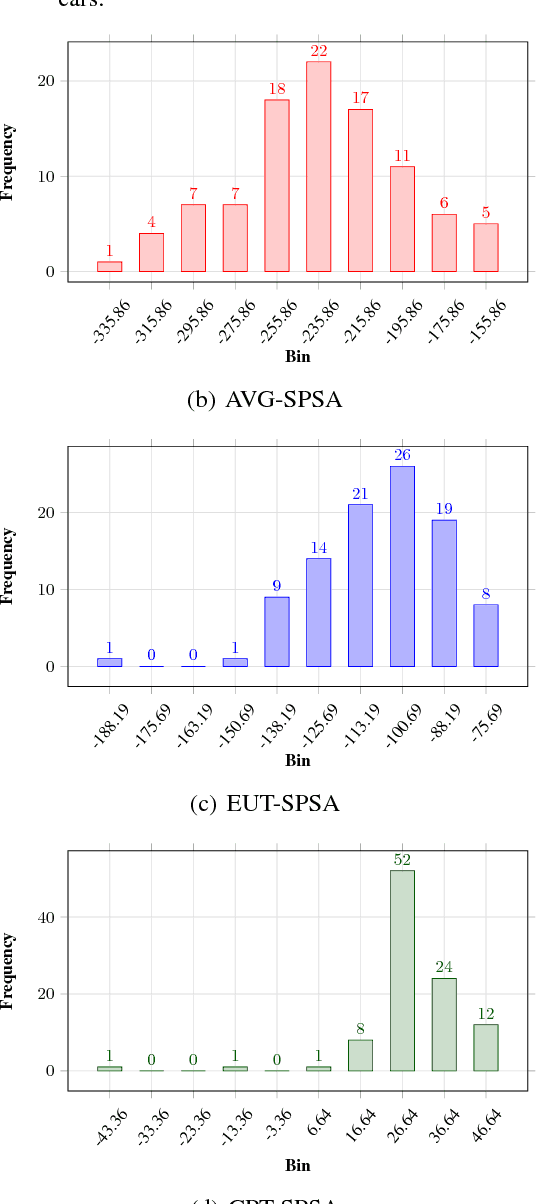
Cumulative prospect theory (CPT) is known to model human decisions well, with substantial empirical evidence supporting this claim. CPT works by distorting probabilities and is more general than the classic expected utility and coherent risk measures. We bring this idea to a risk-sensitive reinforcement learning (RL) setting and design algorithms for both estimation and control. The RL setting presents two particular challenges when CPT is applied: estimating the CPT objective requires estimations of the entire distribution of the value function and finding a randomized optimal policy. The estimation scheme that we propose uses the empirical distribution to estimate the CPT-value of a random variable. We then use this scheme in the inner loop of a CPT-value optimization procedure that is based on the well-known simulation optimization idea of simultaneous perturbation stochastic approximation (SPSA). We provide theoretical convergence guarantees for all the proposed algorithms and also illustrate the usefulness of CPT-based criteria in a traffic signal control application.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge