COVID-Net Biochem: An Explainability-driven Framework to Building Machine Learning Models for Predicting Survival and Kidney Injury of COVID-19 Patients from Clinical and Biochemistry Data
Paper and Code
Apr 24, 2022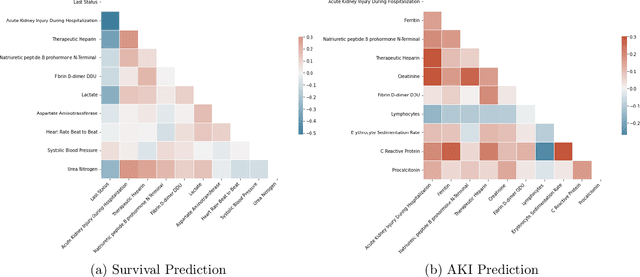
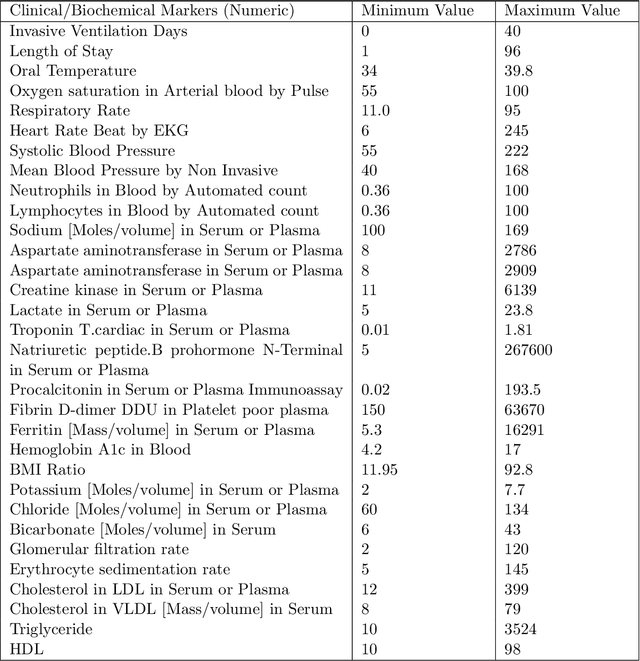
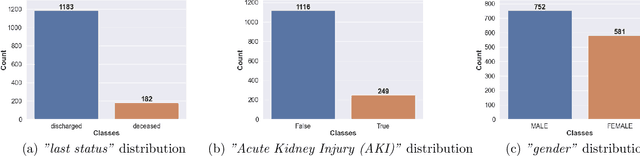
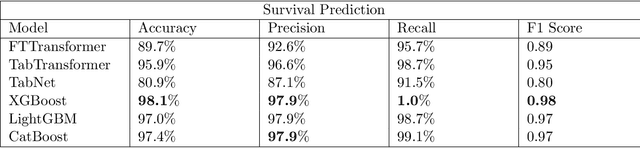
Ever since the declaration of COVID-19 as a pandemic by the World Health Organization in 2020, the world has continued to struggle in controlling and containing the spread of the COVID-19 pandemic caused by the SARS-CoV-2 virus. This has been especially challenging with the rise of the Omicron variant and its subvariants and recombinants, which has led to a significant increase in patients seeking treatment and has put a tremendous burden on hospitals and healthcare systems. A major challenge faced during the pandemic has been the prediction of survival and the risk for additional injuries in individual patients, which requires significant clinical expertise and additional resources to avoid further complications. In this study we propose COVID-Net Biochem, an explainability-driven framework for building machine learning models to predict patient survival and the chance of developing kidney injury during hospitalization from clinical and biochemistry data in a transparent and systematic manner. In the first "clinician-guided initial design" phase, we prepared a benchmark dataset of carefully selected clinical and biochemistry data based on clinician assessment, which were curated from a patient cohort of 1366 patients at Stony Brook University. A collection of different machine learning models with a diversity of gradient based boosting tree architectures and deep transformer architectures was designed and trained specifically for survival and kidney injury prediction based on the carefully selected clinical and biochemical markers.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge