ConSLT: A Token-level Contrastive Framework for Sign Language Translation
Paper and Code
Apr 11, 2022
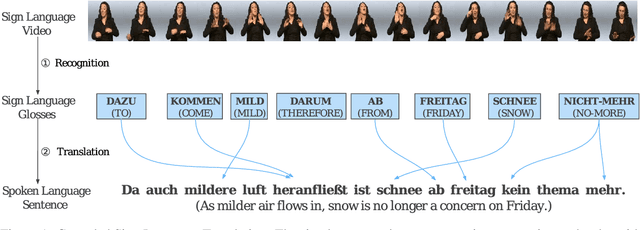

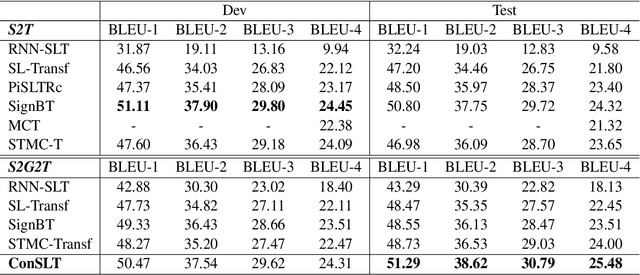
Sign language translation (SLT) is an important technology that can bridge the communication gap between the deaf and the hearing people. SLT task is essentially a low-resource problem due to the scarcity of publicly available parallel data. To this end, inspired by the success of neural machine translation methods based on contrastive learning, we propose ConSLT, a novel token-level \textbf{Con}trastive learning framework for \textbf{S}ign \textbf{L}anguage \textbf{T}ranslation. Unlike previous contrastive learning based works whose goal is to obtain better sentence representation, ConSLT aims to learn effective token representation by pushing apart tokens from different sentences. Concretely, our model follows the two-stage SLT method. First, in the recoginition stage, we use a state-of-the-art continuous sign language recognition model to recognize glosses from sign frames. Then, in the translation stage, we adopt the Transformer framework while introducing contrastive learning. Specifically, we pass each sign glosses to the Transformer model twice to obtain two different hidden layer representations for each token as "positive examples" and randomly sample K tokens that are not in the current sentence from the vocabulary as "negative examples" for each token. Experimental results demonstrate that ConSLT achieves new state-of-the-art performance on PHOENIX14T dataset, with +1.48 BLEU improvements.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge