Confidence-Based Task Prediction in Continual Disease Classification Using Probability Distribution
Paper and Code
Jun 03, 2024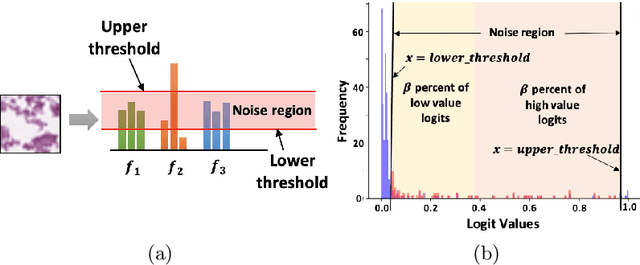
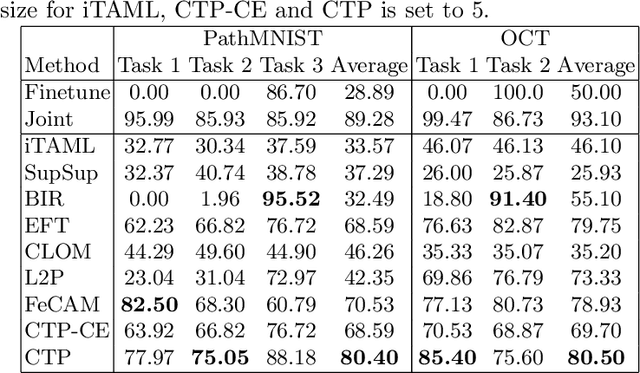
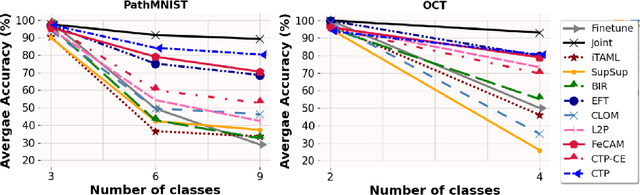
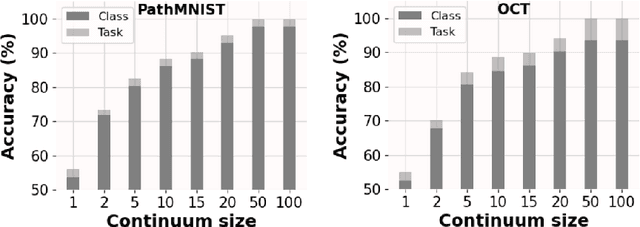
Deep learning models are widely recognized for their effectiveness in identifying medical image findings in disease classification. However, their limitations become apparent in the dynamic and ever-changing clinical environment, characterized by the continuous influx of newly annotated medical data from diverse sources. In this context, the need for continual learning becomes particularly paramount, not only to adapt to evolving medical scenarios but also to ensure the privacy of healthcare data. In our research, we emphasize the utilization of a network comprising expert classifiers, where a new expert classifier is added each time a new task is introduced. We present CTP, a task-id predictor that utilizes confidence scores, leveraging the probability distribution (logits) of the classifier to accurately determine the task-id at inference time. Logits are adjusted to ensure that classifiers yield a high-entropy distribution for data associated with tasks other than their own. By defining a noise region in the distribution and computing confidence scores, CTP achieves superior performance when compared to other relevant continual learning methods. Additionally, the performance of CTP can be further improved by providing it with a continuum of data at the time of inference.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge