Comparing merging behaviors observed in naturalistic data with behaviors generated by a machine learned model
Paper and Code
Apr 21, 2021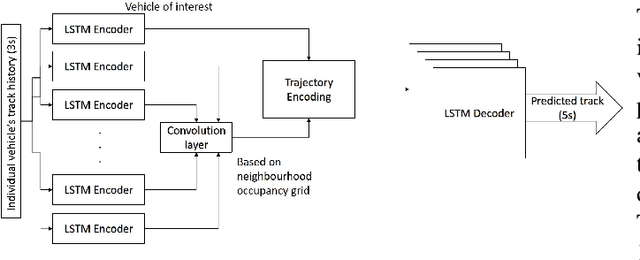
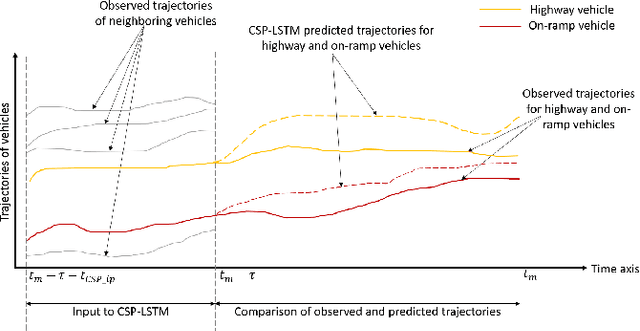
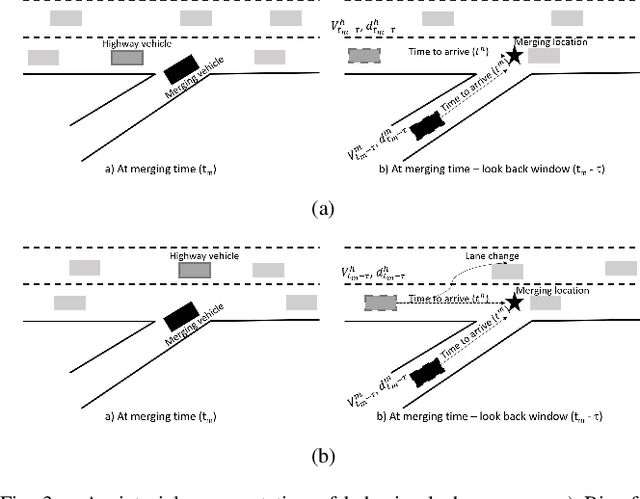
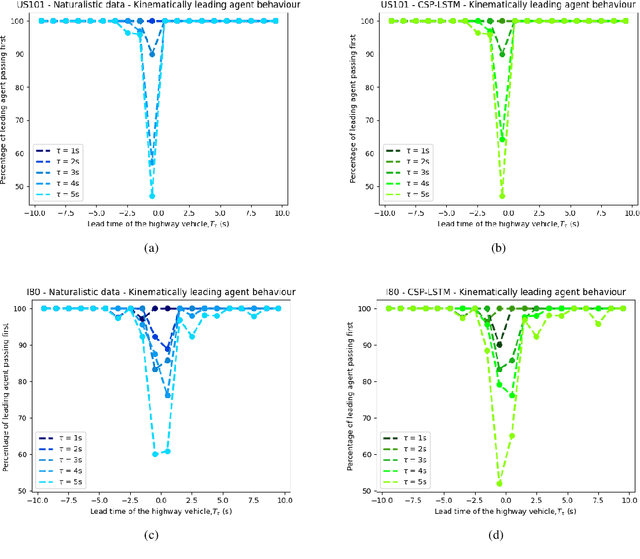
There is quickly growing literature on machine-learned models that predict human driving trajectories in road traffic. These models focus their learning on low-dimensional error metrics, for example average distance between model-generated and observed trajectories. Such metrics permit relative comparison of models, but do not provide clearly interpretable information on how close to human behavior the models actually come, for example in terms of higher-level behavior phenomena that are known to be present in human driving. We study highway driving as an example scenario, and introduce metrics to quantitatively demonstrate the presence, in a naturalistic dataset, of two familiar behavioral phenomena: (1) The kinematics-dependent contest, between on-highway and on-ramp vehicles, of who passes the merging point first. (2) Courtesy lane changes away from the outermost lane, to leave space for a merging vehicle. Applying the exact same metrics to the output of a state-of-the-art machine-learned model, we show that the model is capable of reproducing the former phenomenon, but not the latter. We argue that this type of behavioral analysis provides information that is not available from conventional model-fitting metrics, and that it may be useful to analyze (and possibly fit) models also based on these types of behavioral criteria.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge