CoDeNet: Algorithm-hardware Co-design for Deformable Convolution
Paper and Code
Jun 12, 2020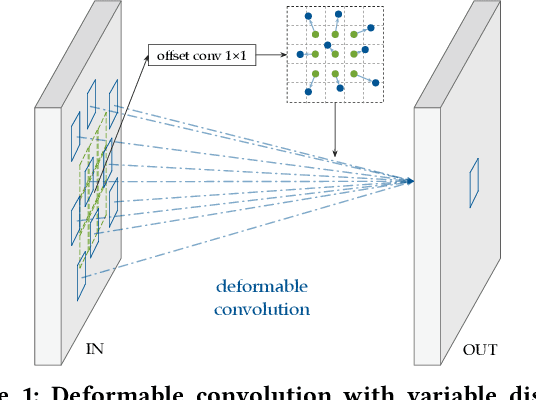
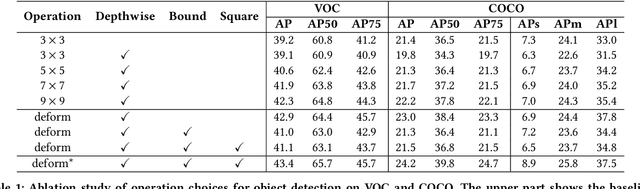
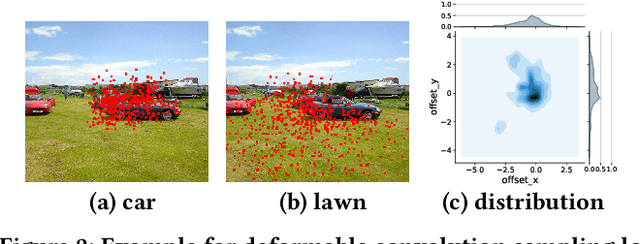
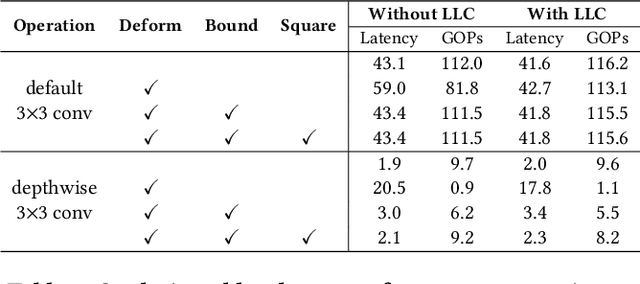
Deploying deep learning models on embedded systems for computer vision tasks has been challenging due to limited compute resources and strict energy budgets. The majority of existing work focuses on accelerating image classification, while other fundamental vision problems, such as object detection, have not been adequately addressed. Compared with image classification, detection problems are more sensitive to the spatial variance of objects, and therefore, require specialized convolutions to aggregate spatial information. To address this, recent work proposes dynamic deformable convolution to augment regular convolutions. Regular convolutions process a fixed grid of pixels across all the spatial locations in an image, while dynamic deformable convolution may access arbitrary pixels in the image and the access pattern is input-dependent and varies per spatial location. These properties lead to inefficient memory accesses of inputs with existing hardware. In this work, we first investigate the overhead of the deformable convolution on embedded FPGA SoCs, and introduce a depthwise deformable convolution to reduce the total number of operations required. We then show the speed-accuracy tradeoffs for a set of algorithm modifications including irregular-access versus limited-range and fixed-shape. We evaluate these algorithmic changes with corresponding hardware optimizations. Results show a 1.36x and 9.76x speedup respectively for the full and depthwise deformable convolution on the embedded FPGA accelerator with minor accuracy loss on the object detection task. We then co-design an efficient network CoDeNet with the modified deformable convolution for object detection and quantize the network to 4-bit weights and 8-bit activations. Results show that our designs lie on the pareto-optimal front of the latency-accuracy tradeoff for the object detection task on embedded FPGAs
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge