CNN-based MultiChannel End-to-End Speech Recognition for everyday home environments
Paper and Code
Nov 07, 2018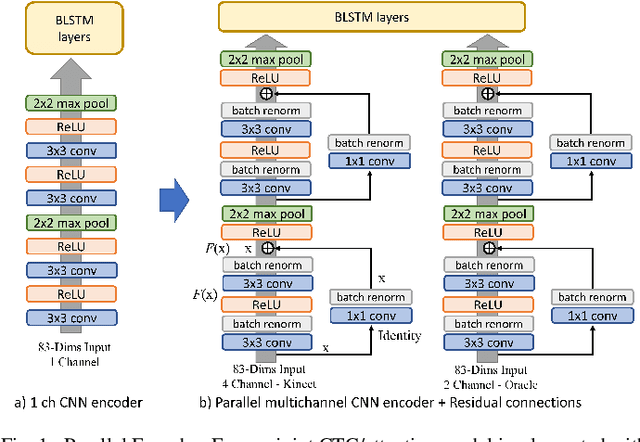
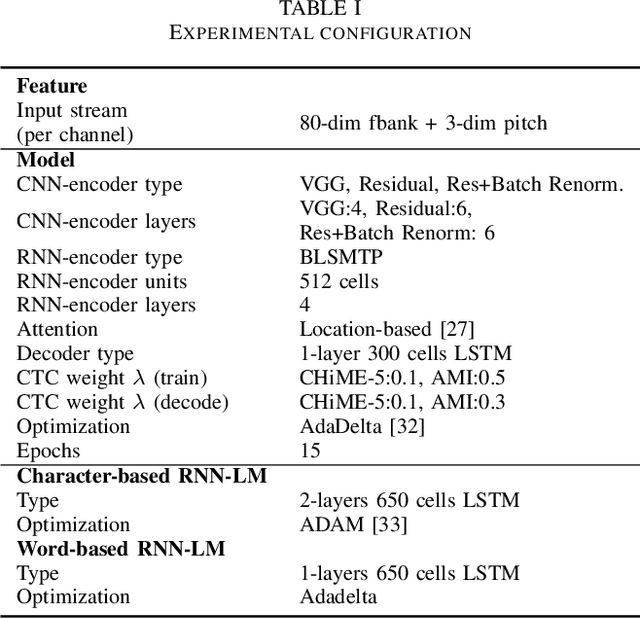
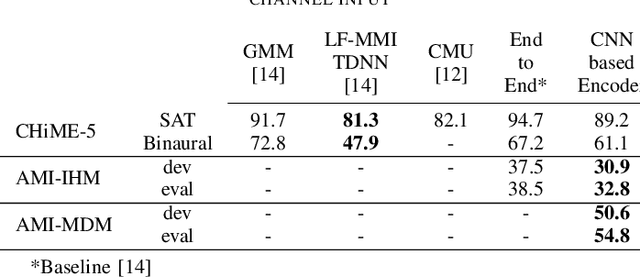
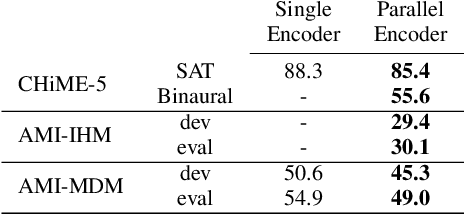
Casual conversations involving multiple speakers and noises from surrounding devices are part of everyday environments and pose challenges for automatic speech recognition systems. These challenges in speech recognition are target for the CHiME-5 challenge. In the present study, an attempt is made to overcome these challenges by employing a convolutional neural network (CNN)-based multichannel end-to-end speech recognition system. The system comprises an attention-based encoder-decoder neural network that directly generates a text as an output from a sound input. The mulitchannel CNN encoder, which uses residual connections and batch renormalization, is trained with augmented data, including white noise injection. The experimental results show that the word error rate (WER) was reduced by 11.9% absolute from the end-to-end baseline.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge