CM-Diff: A Single Generative Network for Bidirectional Cross-Modality Translation Diffusion Model Between Infrared and Visible Images
Paper and Code
Mar 12, 2025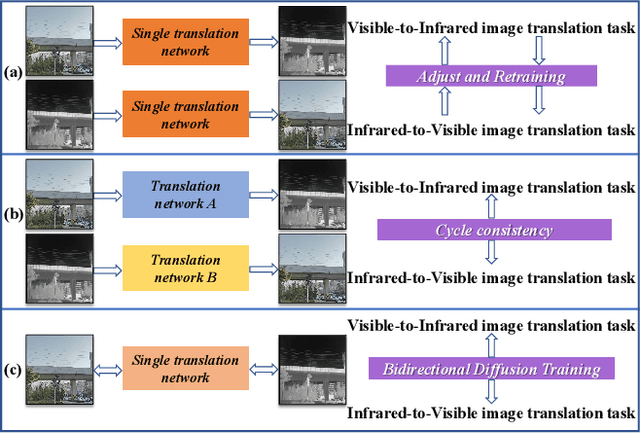
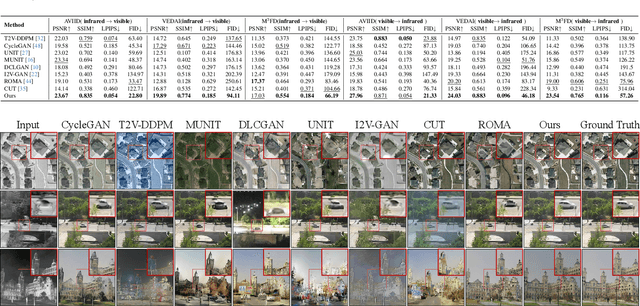
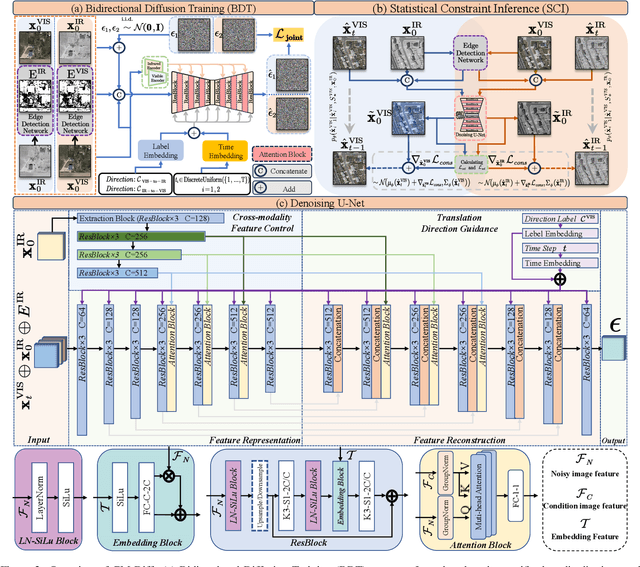
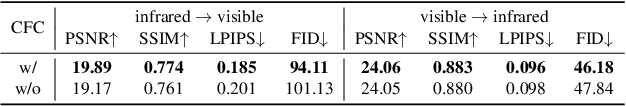
The image translation method represents a crucial approach for mitigating information deficiencies in the infrared and visible modalities, while also facilitating the enhancement of modality-specific datasets. However, existing methods for infrared and visible image translation either achieve unidirectional modality translation or rely on cycle consistency for bidirectional modality translation, which may result in suboptimal performance. In this work, we present the cross-modality translation diffusion model (CM-Diff) for simultaneously modeling data distributions in both the infrared and visible modalities. We address this challenge by combining translation direction labels for guidance during training with cross-modality feature control. Specifically, we view the establishment of the mapping relationship between the two modalities as the process of learning data distributions and understanding modality differences, achieved through a novel Bidirectional Diffusion Training (BDT) strategy. Additionally, we propose a Statistical Constraint Inference (SCI) strategy to ensure the generated image closely adheres to the data distribution of the target modality. Experimental results demonstrate the superiority of our CM-Diff over state-of-the-art methods, highlighting its potential for generating dual-modality datasets.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge