CLIPVQA:Video Quality Assessment via CLIP
Paper and Code
Jul 06, 2024
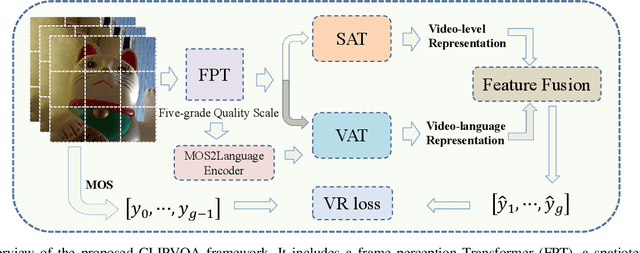
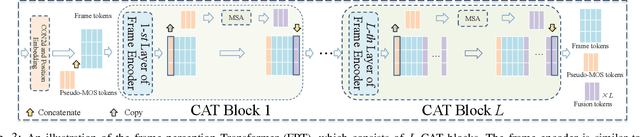
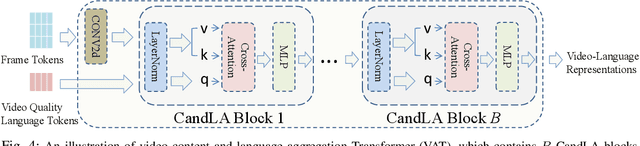
In learning vision-language representations from web-scale data, the contrastive language-image pre-training (CLIP) mechanism has demonstrated a remarkable performance in many vision tasks. However, its application to the widely studied video quality assessment (VQA) task is still an open issue. In this paper, we propose an efficient and effective CLIP-based Transformer method for the VQA problem (CLIPVQA). Specifically, we first design an effective video frame perception paradigm with the goal of extracting the rich spatiotemporal quality and content information among video frames. Then, the spatiotemporal quality features are adequately integrated together using a self-attention mechanism to yield video-level quality representation. To utilize the quality language descriptions of videos for supervision, we develop a CLIP-based encoder for language embedding, which is then fully aggregated with the generated content information via a cross-attention module for producing video-language representation. Finally, the video-level quality and video-language representations are fused together for final video quality prediction, where a vectorized regression loss is employed for efficient end-to-end optimization. Comprehensive experiments are conducted on eight in-the-wild video datasets with diverse resolutions to evaluate the performance of CLIPVQA. The experimental results show that the proposed CLIPVQA achieves new state-of-the-art VQA performance and up to 37% better generalizability than existing benchmark VQA methods. A series of ablation studies are also performed to validate the effectiveness of each module in CLIPVQA.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge