Clicking Matters:Towards Interactive Human Parsing
Paper and Code
Nov 11, 2021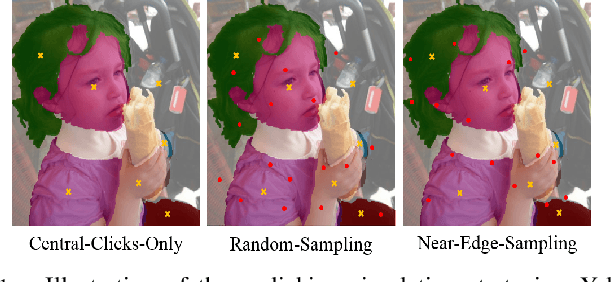
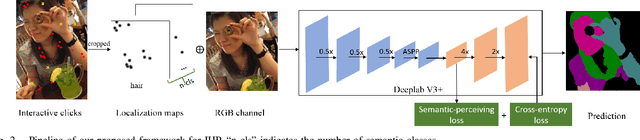
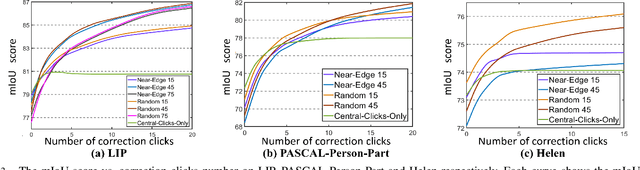
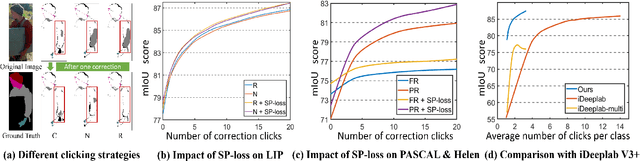
In this work, we focus on Interactive Human Parsing (IHP), which aims to segment a human image into multiple human body parts with guidance from users' interactions. This new task inherits the class-aware property of human parsing, which cannot be well solved by traditional interactive image segmentation approaches that are generally class-agnostic. To tackle this new task, we first exploit user clicks to identify different human parts in the given image. These clicks are subsequently transformed into semantic-aware localization maps, which are concatenated with the RGB image to form the input of the segmentation network and generate the initial parsing result. To enable the network to better perceive user's purpose during the correction process, we investigate several principal ways for the refinement, and reveal that random-sampling-based click augmentation is the best way for promoting the correction effectiveness. Furthermore, we also propose a semantic-perceiving loss (SP-loss) to augment the training, which can effectively exploit the semantic relationships of clicks for better optimization. To the best knowledge, this work is the first attempt to tackle the human parsing task under the interactive setting. Our IHP solution achieves 85\% mIoU on the benchmark LIP, 80\% mIoU on PASCAL-Person-Part and CIHP, 75\% mIoU on Helen with only 1.95, 3.02, 2.84 and 1.09 clicks per class respectively. These results demonstrate that we can simply acquire high-quality human parsing masks with only a few human effort. We hope this work can motivate more researchers to develop data-efficient solutions to IHP in the future.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge