Center-of-Mass-based Robust Grasp Pose Adaptation Using RGBD Camera and Force/Torque Sensing
Paper and Code
May 02, 2022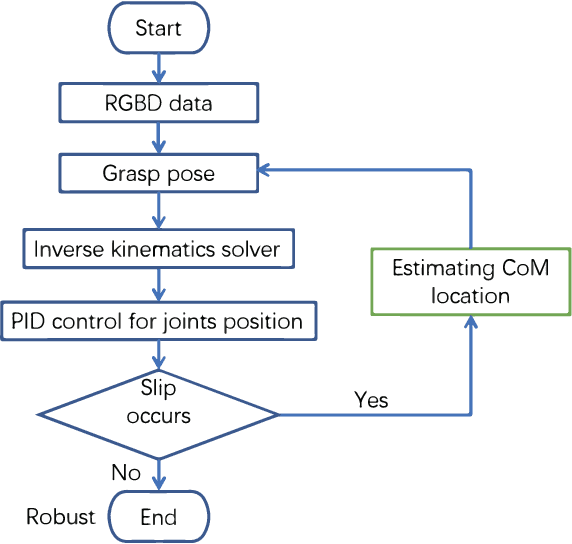
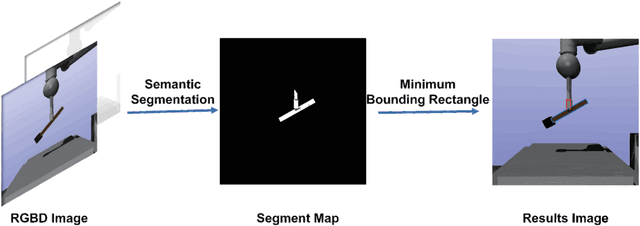
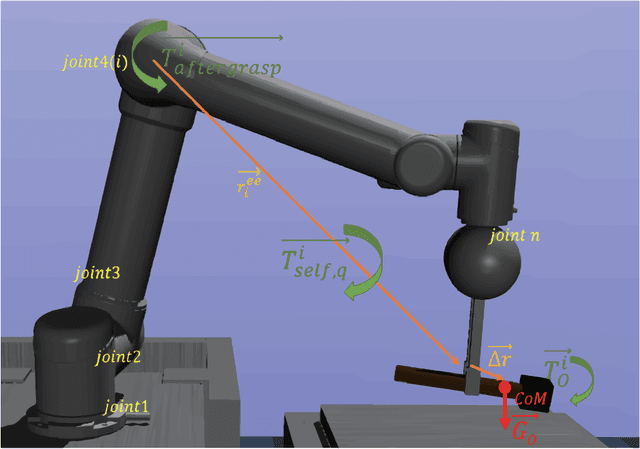
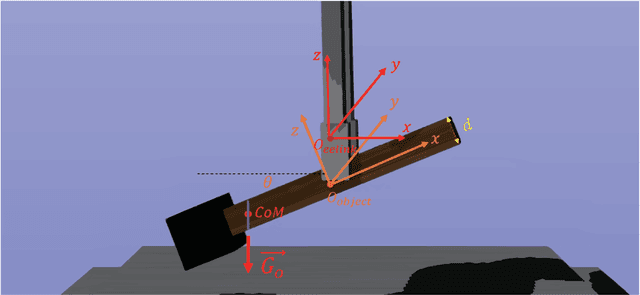
Object dropping may occur when the robotic arm grasps objects with uneven mass distribution due to additional moments generated by objects' gravity. To solve this problem, we present a novel work that does not require extra wrist and tactile sensors and large amounts of experiments for learning. First, we obtain the center-of-mass position of the rod object using the widely fixed joint torque sensors on the robot arm and RGBD camera. Further, we give the strategy of grasping to improve grasp stability. Simulation experiments are performed in "Mujoco". Results demonstrate that our work is effective in enhancing grasping robustness.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge