Center-Embedding and Constituency in the Brain and a New Characterization of Context-Free Languages
Paper and Code
Jun 27, 2022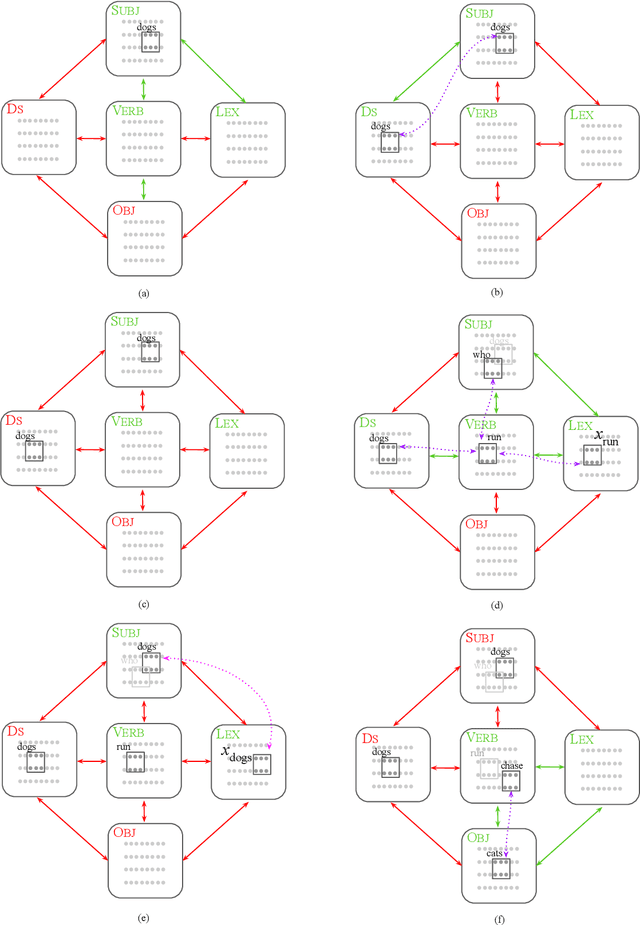
A computational system implemented exclusively through the spiking of neurons was recently shown capable of syntax, that is, of carrying out the dependency parsing of simple English sentences. We address two of the most important questions left open by that work: constituency (the identification of key parts of the sentence such as the verb phrase) and the processing of dependent sentences, especially center-embedded ones. We show that these two aspects of language can also be implemented by neurons and synapses in a way that is compatible with what is known, or widely believed, about the structure and function of the language organ. Surprisingly, the way we implement center embedding points to a new characterization of context-free languages.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge