CataNet: Predicting remaining cataract surgery duration
Paper and Code
Jun 21, 2021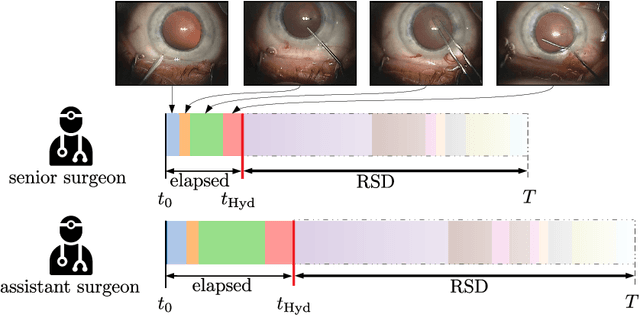
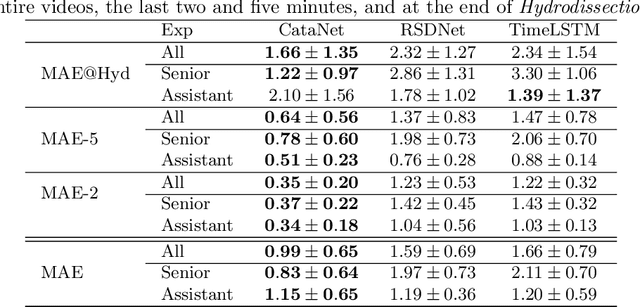
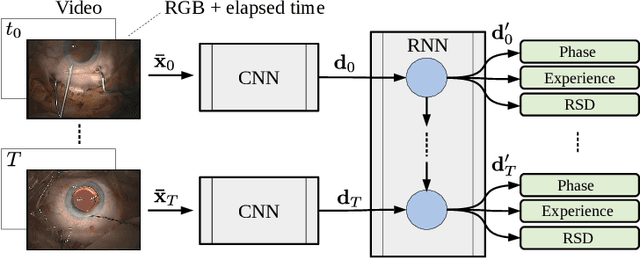

Cataract surgery is a sight saving surgery that is performed over 10 million times each year around the world. With such a large demand, the ability to organize surgical wards and operating rooms efficiently is critical to delivery this therapy in routine clinical care. In this context, estimating the remaining surgical duration (RSD) during procedures is one way to help streamline patient throughput and workflows. To this end, we propose CataNet, a method for cataract surgeries that predicts in real time the RSD jointly with two influential elements: the surgeon's experience, and the current phase of the surgery. We compare CataNet to state-of-the-art RSD estimation methods, showing that it outperforms them even when phase and experience are not considered. We investigate this improvement and show that a significant contributor is the way we integrate the elapsed time into CataNet's feature extractor.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge