BRACS: A Dataset for BReAst Carcinoma Subtyping in H&E Histology Images
Paper and Code
Nov 08, 2021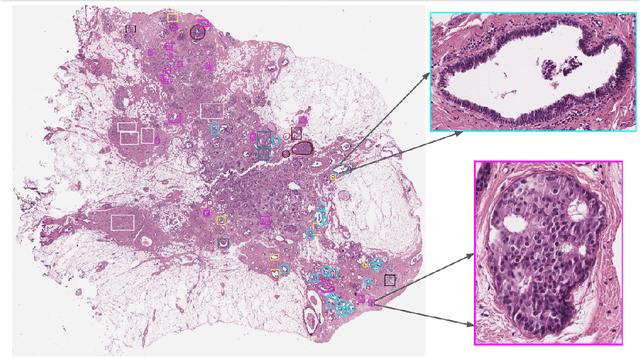
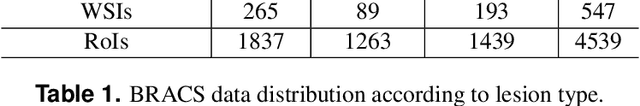
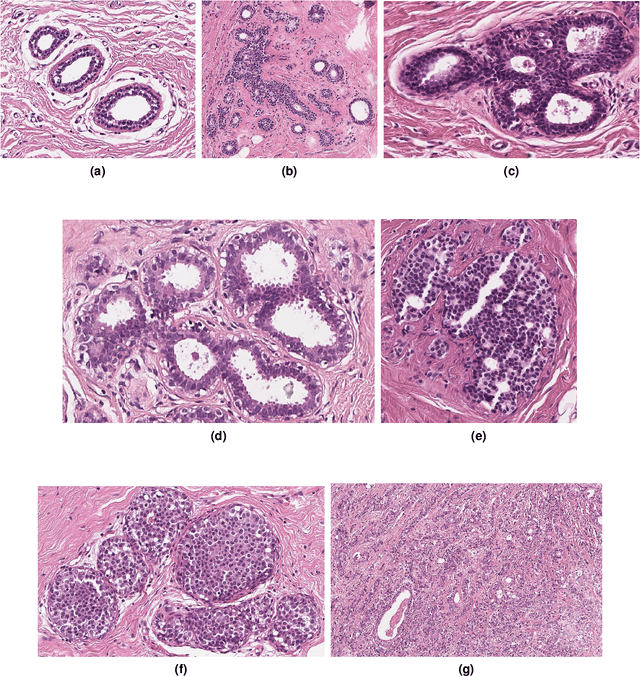
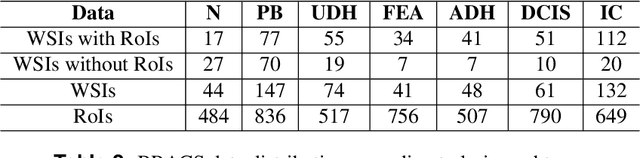
Breast cancer is the most commonly diagnosed cancer and registers the highest number of deaths for women with cancer. Recent advancements in diagnostic activities combined with large-scale screening policies have significantly lowered the mortality rates for breast cancer patients. However, the manual inspection of tissue slides by the pathologists is cumbersome, time-consuming, and is subject to significant inter- and intra-observer variability. Recently, the advent of whole-slide scanning systems have empowered the rapid digitization of pathology slides, and enabled to develop digital workflows. These advances further enable to leverage Artificial Intelligence (AI) to assist, automate, and augment pathological diagnosis. But the AI techniques, especially Deep Learning (DL), require a large amount of high-quality annotated data to learn from. Constructing such task-specific datasets poses several challenges, such as, data-acquisition level constrains, time-consuming and expensive annotations, and anonymization of private information. In this paper, we introduce the BReAst Carcinoma Subtyping (BRACS) dataset, a large cohort of annotated Hematoxylin & Eosin (H&E)-stained images to facilitate the characterization of breast lesions. BRACS contains 547 Whole-Slide Images (WSIs), and 4539 Regions of Interest (ROIs) extracted from the WSIs. Each WSI, and respective ROIs, are annotated by the consensus of three board-certified pathologists into different lesion categories. Specifically, BRACS includes three lesion types, i.e., benign, malignant and atypical, which are further subtyped into seven categories. It is, to the best of our knowledge, the largest annotated dataset for breast cancer subtyping both at WSI- and ROI-level. Further, by including the understudied atypical lesions, BRACS offers an unique opportunity for leveraging AI to better understand their characteristics.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge