Benchmarking ML Approaches to UWB-Based Range-Only Posture Recognition for Human Robot-Interaction
Paper and Code
Aug 28, 2024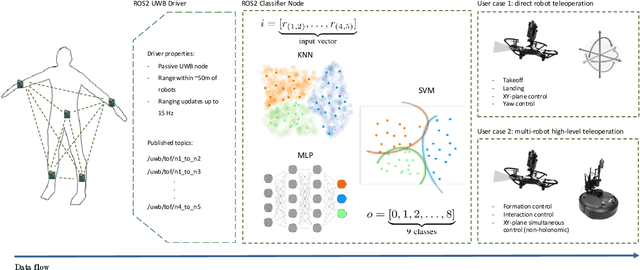
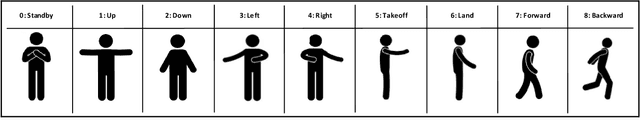
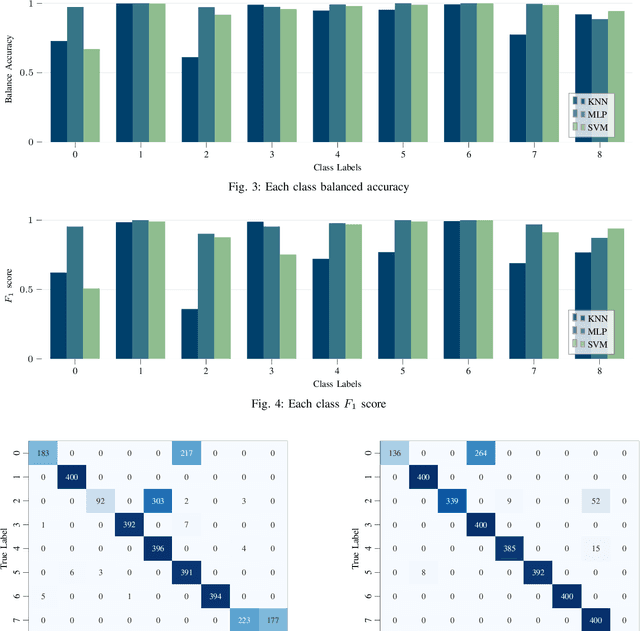
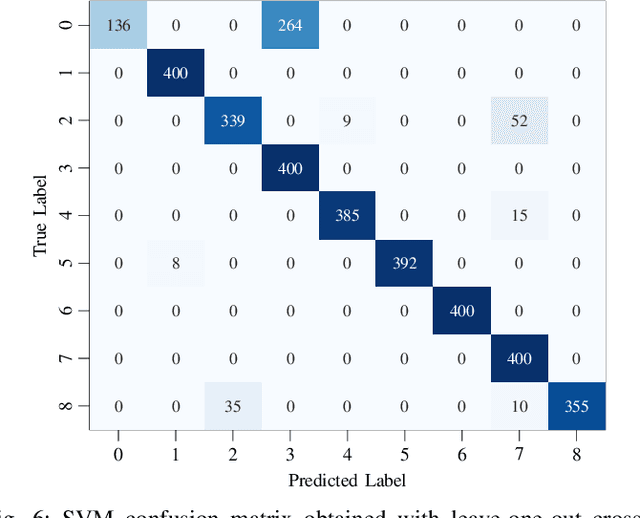
Human pose estimation involves detecting and tracking the positions of various body parts using input data from sources such as images, videos, or motion and inertial sensors. This paper presents a novel approach to human pose estimation using machine learning algorithms to predict human posture and translate them into robot motion commands using ultra-wideband (UWB) nodes, as an alternative to motion sensors. The study utilizes five UWB sensors implemented on the human body to enable the classification of still poses and more robust posture recognition. This approach ensures effective posture recognition across a variety of subjects. These range measurements serve as input features for posture prediction models, which are implemented and compared for accuracy. For this purpose, machine learning algorithms including K-Nearest Neighbors (KNN), Support Vector Machine (SVM), and deep Multi-Layer Perceptron (MLP) neural network are employed and compared in predicting corresponding postures. We demonstrate the proposed approach for real-time control of different mobile/aerial robots with inference implemented in a ROS 2 node. Experimental results demonstrate the efficacy of the approach, showcasing successful prediction of human posture and corresponding robot movements with high accuracy.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge