Balancing Simulation-based Inference for Conservative Posteriors
Paper and Code
Apr 21, 2023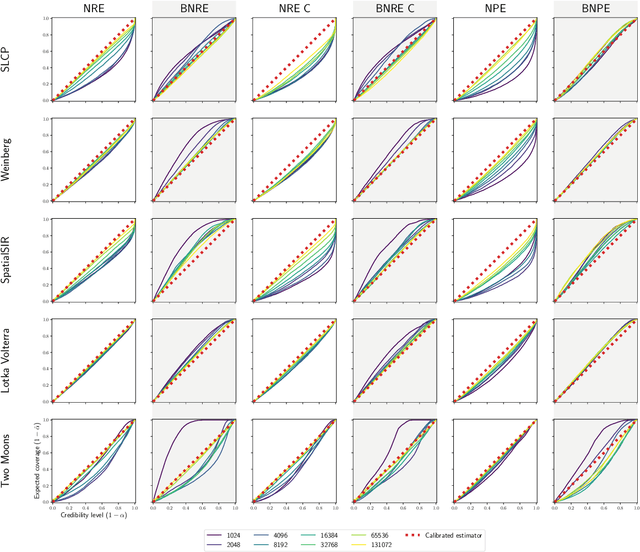
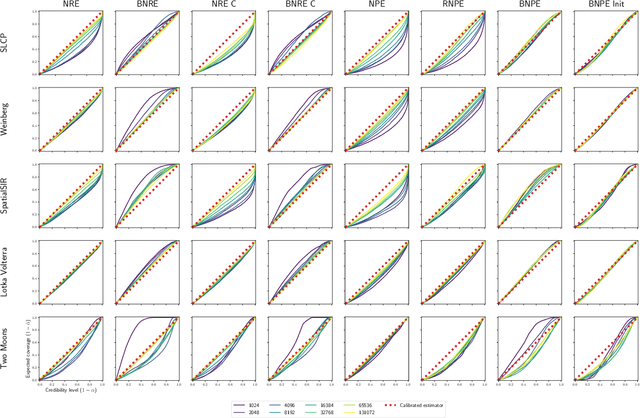
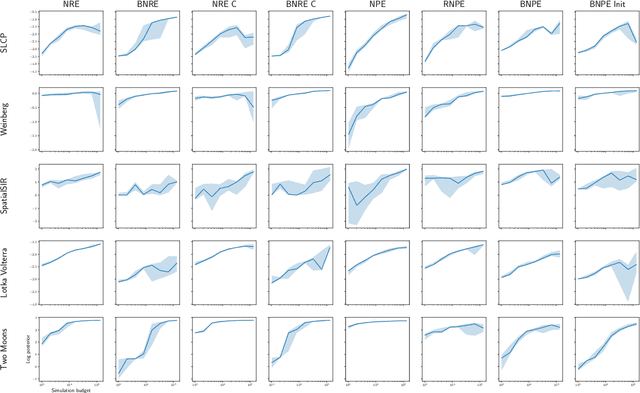
Conservative inference is a major concern in simulation-based inference. It has been shown that commonly used algorithms can produce overconfident posterior approximations. Balancing has empirically proven to be an effective way to mitigate this issue. However, its application remains limited to neural ratio estimation. In this work, we extend balancing to any algorithm that provides a posterior density. In particular, we introduce a balanced version of both neural posterior estimation and contrastive neural ratio estimation. We show empirically that the balanced versions tend to produce conservative posterior approximations on a wide variety of benchmarks. In addition, we provide an alternative interpretation of the balancing condition in terms of the $\chi^2$ divergence.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge