Back to the Manifold: Recovering from Out-of-Distribution States
Paper and Code
Jul 18, 2022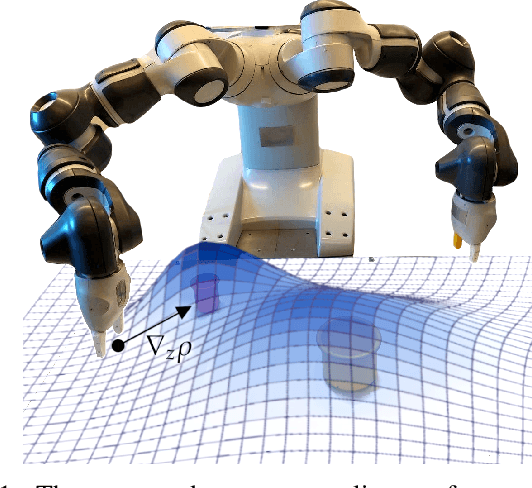
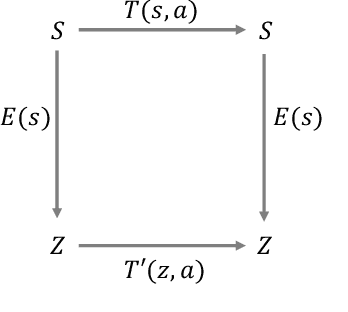
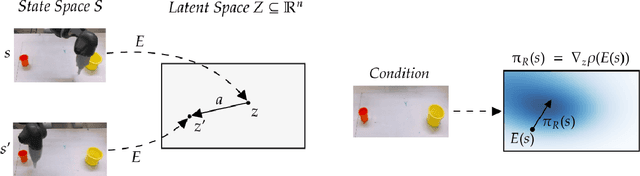
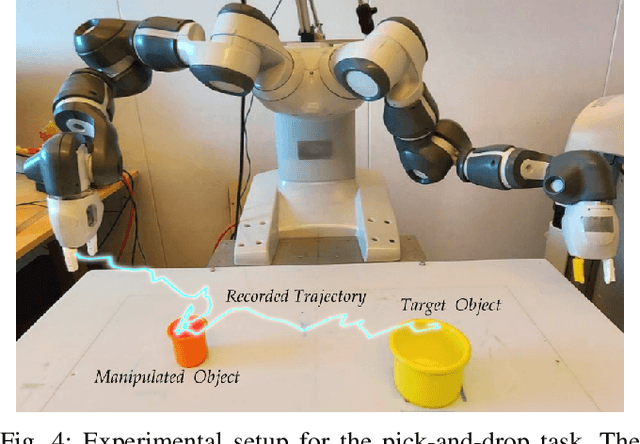
Learning from previously collected datasets of expert data offers the promise of acquiring robotic policies without unsafe and costly online explorations. However, a major challenge is a distributional shift between the states in the training dataset and the ones visited by the learned policy at the test time. While prior works mainly studied the distribution shift caused by the policy during the offline training, the problem of recovering from out-of-distribution states at the deployment time is not very well studied yet. We alleviate the distributional shift at the deployment time by introducing a recovery policy that brings the agent back to the training manifold whenever it steps out of the in-distribution states, e.g., due to an external perturbation. The recovery policy relies on an approximation of the training data density and a learned equivariant mapping that maps visual observations into a latent space in which translations correspond to the robot actions. We demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed method through several manipulation experiments on a real robotic platform. Our results show that the recovery policy enables the agent to complete tasks while the behavioral cloning alone fails because of the distributional shift problem.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge