Automatic dense annotation of large-vocabulary sign language videos
Paper and Code
Aug 04, 2022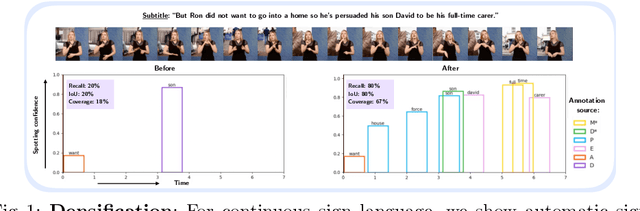

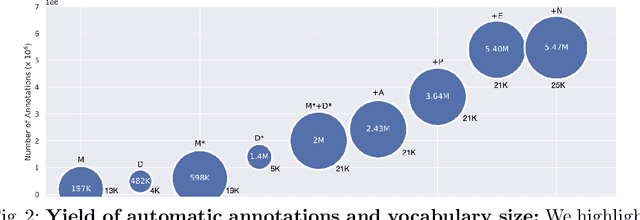
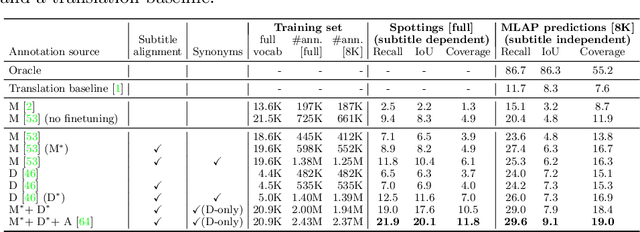
Recently, sign language researchers have turned to sign language interpreted TV broadcasts, comprising (i) a video of continuous signing and (ii) subtitles corresponding to the audio content, as a readily available and large-scale source of training data. One key challenge in the usability of such data is the lack of sign annotations. Previous work exploiting such weakly-aligned data only found sparse correspondences between keywords in the subtitle and individual signs. In this work, we propose a simple, scalable framework to vastly increase the density of automatic annotations. Our contributions are the following: (1) we significantly improve previous annotation methods by making use of synonyms and subtitle-signing alignment; (2) we show the value of pseudo-labelling from a sign recognition model as a way of sign spotting; (3) we propose a novel approach for increasing our annotations of known and unknown classes based on in-domain exemplars; (4) on the BOBSL BSL sign language corpus, we increase the number of confident automatic annotations from 670K to 5M. We make these annotations publicly available to support the sign language research community.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge